Oracle Applications R12 Architecture

In EBS R12, various servers or services are distributed among the following three levels, or tiers.
- The Desktop Tier
- The Application Tier
- The Database Tier
1] The Desktop Tier
The client interface is provided through HTML for HTML-based applications, and via a Java applet in a Web browser for the traditional Forms-based applications.
In Oracle Applications Release 12, each user logs in to Oracle Applications through the E-Business Suite Home Page on a desktop client web browser. The E-Business Suite Home Page provides a single point of access to HTML-based applications, Forms-based applications, and Business Intelligence applications.
Oracle JInitiator will no longer be required to run Oracle Forms in E-Business Suite Release 12. Oracle Forms in Release 12 will run directly in the native Sun Java2 Standard Edition plug-in.
The Forms client applet is a general-purpose presentation applet that supports all Oracle Applications Forms-based products, including those with customizations and extensions. The Forms client applet is packaged as a collection of Java Archive (JAR) files. The JAR files contain all Java classes required to run the presentation layer of Oracle Applications forms.
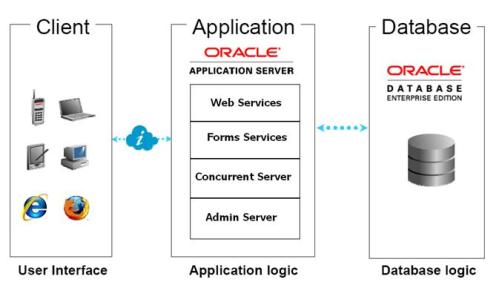
2] The Application Tier
The application tier has a dual role: hosting the various servers and service groups that process the business logic, and managing communication between the desktop tier and the database tier. This tier is sometimes referred to as the middle tier.
Four servers or service groups comprise the basic application tier for Oracle Applications:
- Web services
- Forms services
- Concurrent Processing server
- Admin server
3] The Database Tier
The database tier contains the Oracle database server, which stores all the data maintained by Oracle Applications. The database also stores the Oracle Applications online help information. More specifically, the database tier contains the Oracle data server files and Oracle Applications database executables that physically store the tables, indexes, and other database objects for your system. The database server does not communicate directly with the desktop clients, but rather with the servers on the application tier, which mediate the communications between the database server and the clients.

Leave a Reply
Want to join the discussion?Feel free to contribute!