-
EBS 12.2 represents our most-groundbreaking release in years (Press Release). It includes new product functionality, new Fusion Middleware and database components, and introduces new tools for installing, configuring, and maintaining E-Business Suite environments:
Hundreds of new features
Includes significant enhancements across the integrated suite of business applications spanning enterprise resource planning, human capital management, and supply chain management. You can find the complete list here:- E-Business Suite 12.2 Release Content Document (Note 1302189.1)
Online PatchingApply EBS patches while users are still entering transactions and using the E-Business Suite. Online Patching uses the Oracle Database’s Edition-Based Redefinition feature and other new technologies to allow the E-Business Suite to be updated while the system is still running. You can learn more about Online Patching via our official documentation and this technical webcast.WebLogic ServerUses Oracle WebLogic Server, which replaces the Oracle Containers for Java (OC4J) application server used in EBS 12.0 and 12.1. You can learn more about how this improves the system administration experience via our official documentation and this technical webcast.Streamlined installation
- Option for installing EBS 12.2 on to existing database servers.
- Capability of installation into existing Real Application Clusters environments.
- Database deployment on Automatic Storage Management (ASM) and other file systems.
Upgrading to EBS 12.2Is there a direct upgrade path from EBS 11i to 12.2?Yes, there is a direct upgrade path from EBS 11.5.10.2 to EBS 12.2. EBS 11.5.10.2 customers do not have to install an intermediary EBS 12 release (such as 12.1.3) before upgrading to EBS 12.2. EBS 11.5.10.2 customers must have applied the minimum baseline patch requirements for Extended Support as described in Patch Requirements for Extended Support of Oracle E-Business Suite Release 11.5.10 (Document 883202.1). Customers on earlier EBS 11i releases (such as 11.5.7) need to be at the 11.5.10.2 level plus the minimum baseline patch requirements for Extended Support before they can upgrade to EBS 12.2.Is there a direct upgrade path from EBS 12.0 to 12.2?Yes, there is a direct upgrade path from EBS 12.0.4 and 12.0.6 to EBS 12.2. EBS 12.0.4 or 12.0.6 customers do not have to install an intermediary EBS 12 release (such as 12.1.3) before upgrading to EBS 12.2. Customers on earlier EBS 12.0 releases (such as 12.0.3) will need to be at the 12.0.4 or 12.0.6 level before they can upgrade to EBS 12.2.Is there a direct upgrade path from EBS 12.1 to 12.2?Yes, there is a direct upgrade path from EBS 12.1.1, 12.1.2, and 12.1.3 to EBS 12.2.How can I prepare for EBS 12.2?- Read the Oracle E-Business Suite 12.2 Technical Planning Guide, First Edition (Note 1585857.1)
More technical references- EBS 12.2 Product Information Center (Note 1581299.1)
- EBS 12.2 Documentation Library (Oracle Technology Network)
Responsibility – Payables Manager
Navigation – Invoices – Entry – Open Interface Invoices

Clicking on the above link, opens the below form ..

Open the Query-mode to view the Invoice in the Interface table

Above is the header line. Click on Lines to view the lines information.
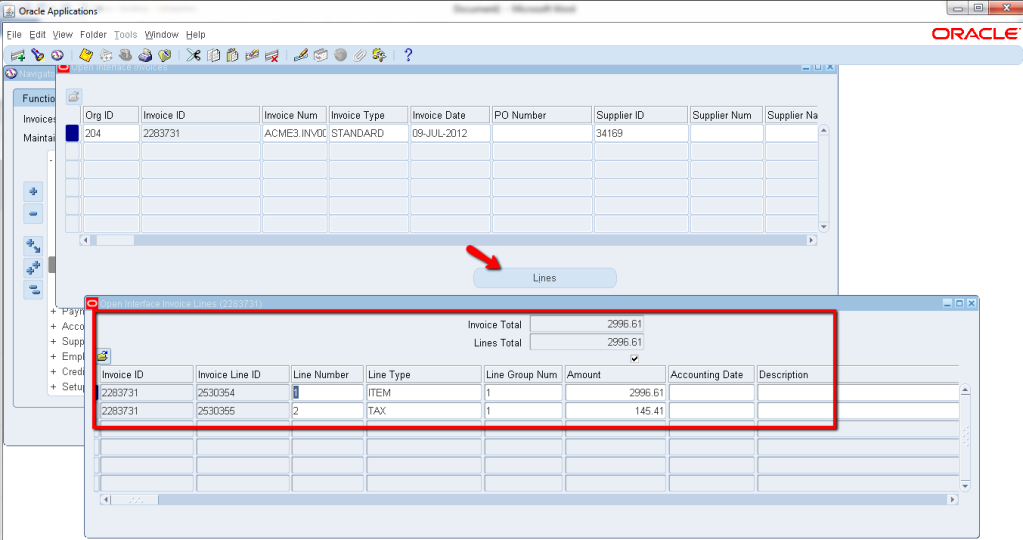
This would avoid looking for Invoices by querying in the back-end.
1. Develop the report as per client requirement using the Report-6i tool.
2. Move the report (.rdf) file from local machine to respective path in the server. If client have the CUST_TOP then move into Cust_Top else move it to the related Standard Top.Custom Top – CUST_TOP/ 11.5.0/ Report/ US/ .rdf Standard Top – PO_TOP/ 11.5.0/ Report/ US/ .rdf (For PO report)
3. Create “Executable” for that report (After log on to Oracle Applications and Select “System Administrator” responsibility)
4. Create “Concurrent Program” and attach Executable to Conc. Prgm. and define Parameters and Incompatibles if any.Concurrent Program: It is an instance of the executable file along with parameters & incompatible.
5. Create “Request Group” and attach Conc. Prgm. to Request Group.Request Group is nothing but a collection of Conc. Prgms.
6. Create “Responsibility” and attach the Request Group to Responsibility.
7. Create “User” attach Responsibility to User”
so that the user can run this Conc. Prgm. form the “SRS Window” (Standard Request Submission).
Note: All the Conc. Prgms. should run from the SRS window (Even if we run from Back-End)By default the user has the rights of System Administrator or Application Developer responsibilities
Every form in Oracle Applications contains 3-Types of Fields.
1. Yellow color – Mandatory2. Green Color – Read-Only3. White Color – Optional
How to Create New User in Oracle Apps?
User Creation: Open IE and type path of Oracle Application in address bar enter User Name and Password
User Name: OPERATIONS Password: WELCOME
Select System Administrator Responsibility
Select Security / User / Define Give the required information and Save.
Switch the user to newly created User.
Note: When we create any User, the User stored at FND_USER.
How we can find the Table names of Apps Screen?
We can find through Help => Record-History => FND_USER
How to find Column Name from front end Apps Screen :
To find all column names: Help => Diagnostics => Examine
What is WHO Columns and How many WHO Columns in Oracle Apps?
Ans : 4 types of who columns for each table in Oracle Applications
Created By Creation Date Updated By Updated Date
2.1. Intercompany Invoicing Cycle
When a sales order is entered in an operating unit, and if the shipping warehouse is part of a separate operating unit (may also belong to another SOB), then the goods can be shipped from the said shipping organization and the selling organization generates a customer invoice. Also the system automatically records an intercompany sale between the shipping organization and the selling organization by generating intercompany invoices. This is called Intercompany invoicing.

After entering the order in Selling operating unit, you can pick release and ship confirm the order from Shipping Operating unit. Then the following programs need to be run to ensure necessary Intercompany invoices are created ..
- Launch the Cost Manager in Inventory > Setup > Transactions > Interface Managers. If it is not active then go to Tools and Launch Manager. Intercompany Invoices will not be generated unless this manager is active.
- In Shipping OU run ‘Create Intercompany AR Invoices’. Ensure that the items shipped have a price for ‘Internal Price List’.
- In Shipping OU run ‘Receivables AutoInvoice Program’
- In Selling OU run ‘Create Intercompany AP Invoices’. Ensure that the conversion rates between the functional currencies of above SOBs exist for the current date and GL period is open in both OUs.
- In selling OU run ‘Expense Report Import’ (Payables)
2.1.1. Transaction Steps
Create an Order in ‘Vision Operations’ OU and schedule it from D1 warehouse under ‘Singapore Distribution Centre’ OU as ..


After Pick release and shipconfirm the order, the delivery associated with the line is closed as ..

- The Create Intercompany AR Invoices process creates invoice lines for order shipment transactions in Oracle Inventory where the shipping warehouse does not belong to the order entry operating unit.
- The Oracle Receivables AutoInvoice program processes the records inserted into the interface tables by the Create Intercompany AR Invoices process.
- Find the AR Invoice that has been generated in Shipping OU by querying for source ‘Intercompany’ and optionally by the Sales Order.

- Create Intercompany AP Invoices process creates records in Payable invoices interface tables.
- The Oracle Payables ‘Expense Report Import’ program processes the records inserted into the interface tables by the Create Intercompany AP Invoices process. All invoices created by the Create Intercompany AP Invoices program have Intercompany as their source.
- Find the Payables Invoice that has been generated in Selling OU by querying for supplier and today’s date.

- The customer invoice automatically gets created if the ‘Workflow background process’ is running. Find it in Selling OU by querying for the transaction source as ‘ORDER ENTRY’ and with a date range.
2.2. Set up steps
The below set-up steps are necessary for proper functioning of Intercompany invoicing cycle ..
- Define a customer and customer site in the selling operating unit.
- Define a supplier and supplier site in the shipping operating unit.
- Define Intercompany Relations
- Define price for the items in ‘Internal Price list’
The organization itself is defined as a customer ‘Vision’, having a customer site in the selling operating unit as ..

The organization itself is defined as a supplier ‘Vision’, with a supplier site in the shipping operating unit as ..

Define Intercompany Relations as ..

Define price for the items in ‘Internal Price list’ ..

Latest Posts
- R12 – How to Handle NULL for :$FLEX$.VALUE_SET_NAME In Oracle ERPAugust 25, 2023 - 1:20 pm
- R12 – How to Delete Oracle AR TransactionsMarch 22, 2019 - 8:37 pm
- How to Define Custom Key Flexfield (KFF) in R12January 19, 2018 - 5:43 pm
- AutoLock Box Concepts In R12November 10, 2017 - 8:30 am
- R12 – java.sql.SQLException: Invalid column type in OAFSeptember 15, 2017 - 9:39 am
| S | M | T | W | T | F | S |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 |
| 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 |
| 15 | 16 | 17 | 18 | 19 | 20 | 21 |
| 22 | 23 | 24 | 25 | 26 | 27 | 28 |
| 29 | 30 | 31 | ||||

Recent Comments