Oracle Purchasing Tables
po_requisition_headers_all
po_requisition_lines_all
po_req_distributions_all
po_headers_all
po_lines_all
po_distributions_all
rcv_transactions
po_requisitions_interface_all
po_reschedule_interface
po_headers_interface
po_lines_interface
po_distributions_interface
po_vendors
po_vendor_sites_all
po_vendor_contacts
Understanding the Matching Tables
Payables uses several of Oracle Purchasing tables for matching. To implement matching in Payables, you need to load these tables with the data from your non-Oracle purchasing application.
- PO_DISTRIBUTIONS_AP_V (view of PO_DISTRIBUTIONS)
- PO_RELEASES (Blanket Purchase Orders)
AutoInstall automatically installs these and other necessary Oracle Purchasing application tables when you install Payables.
PO_HEADERS
Each record in this table represents a purchase order, which is an order for goods or services from a single supplier. Each purchase order may have multiple lines (PO_LINES). In addition, each blanket purchase order may have multiple blanket releases (PO_RELEASES), which release an amount from the blanket.
PO_LINES
Each record in this table represents a purchase order line, which identifies the items and unit price for the goods ordered on a purchase order. Each purchase order line may have multiple shipments (PO_LINE_LOCATIONS).
PO_LINE_LOCATIONS
Each record in this table represents a purchase order shipment, which identifies the quantity of an item shipped to a buyer location by the supplier. Each purchase order shipment may have multiple accounting distributions (PO_DISTRIBUTIONS).
PO_DISTRIBUTIONS/PO_DISTRIBUTIONS_AP_V
Each record in this table/view represents a purchase order distribution, which identifies the account charged for the items on a purchase order shipment.
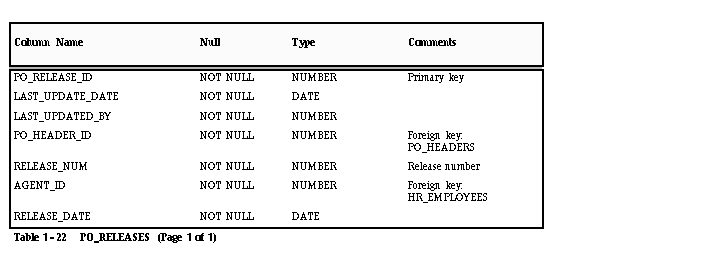
PO_RELEASES
Each record in this table represents a blanket release for a purchase order. A blanket release may create multiple shipments.
AP_INVOICES/AP_INVOICE_DISTRIBUTIONS
Each purchase order shipment can be matched to multiple invoices (AP_INVOICES), and a single invoice may be matched to multiple purchase order shipments. When you match an invoice to a purchase order shipment, Payables creates an invoice distribution (AP_INVOICE_DISTRIBUTIONS) from each purchase order distribution on the shipment. When you match an invoice to a single purchase order distribution, Payables creates a single invoice distribution from the purchase order distribution.
Table Descriptions
The following section describes the tables and the columns that Payables supports for matching to purchase orders from your non-Oracle purchase system. We describe how the columns are used and, if a column is required, the values you must load to successfully perform matching. For a complete description of the tables, please consult the
Payables Applications Technical Reference Manual.
Attention: You must populate all NOT NULL columns in the purchasing tables.
PO_HEADERS
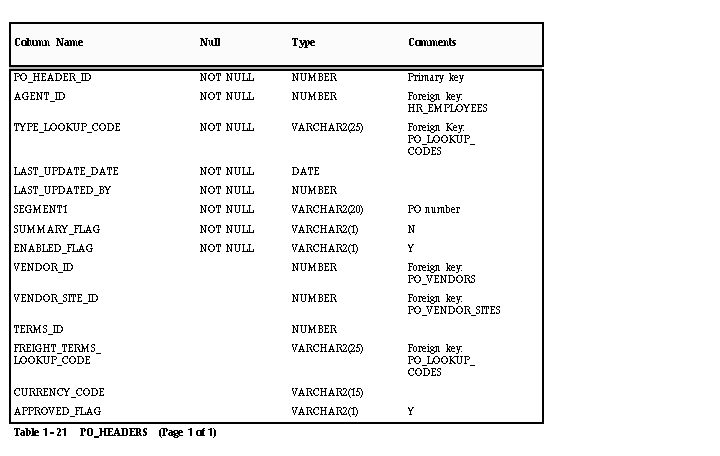
AGENT_ID
Enter the ID for the agent who created the purchase order. This value is used by the following reports in Payables: Merge Suppliers, Matching Agent Notice and Receiving Hold Requestor Notice.
TYPE_LOOKUP_CODE
Enter BLANKET or STANDARD (Lookup Type: PO TYPE) to identify the type of purchase order.
TERMS_ID
Enter the ID for the payment terms of the purchase order. Payables uses this value during matching to warn you if the payment terms on the purchase order do not match the payment terms on the invoice being matched to the purchase order. If you choose to leave this column empty, Payables will not warn you if the purchase order and invoice payment terms differ.
FREIGHT_TERMS_LOOKUP_CODE
Enter a QuickCode (QuickCode Type: FREIGHT TERMS) to identify the freight terms for the purchase order. See: QuickCodes.
CURRENCY_CODE
Enter the currency code for the purchase order. You can obtain a list of valid codes from FND_CURRENCIES.CURRENCY_CODE. The currency code for the invoice you want to match to this purchase order must be the same as the code you enter here.
PO_RELEASES (Blanket releases)
PO_LINES
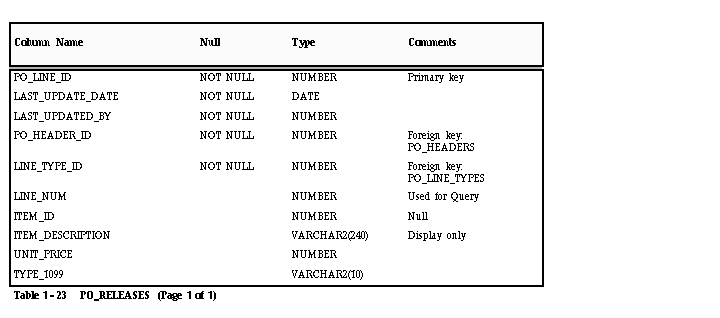
LINE_TYPE_ID
Enter the ID for the line type of the purchase order line. You can obtain a list of valid IDs from PO_LINE_TYPES.LINE_TYPE_ID.
ITEM_ID
Do not enter a value in this column. Payables does not allow you to record purchase order lines with Items unless you install Oracle Purchasing.
ITEM_DESCRIPTION
Enter a description for your purchase order line. You can use this column to record information about the item on the purchase order line. Payables displays this description in the Purchase Order Shipments zone during matching.
TYPE_1099
Enter the income tax type for the purchase order line, if the supplier for the purchase order is a 1099 supplier. Payables assigns this type as the default income tax type for each invoice distribution created by matching to this purchase order line. If you leave the column empty, Payables uses the income tax type for the supplier as the default. You can obtain a list of valid types from AP_INCOME_TAX_TYPES.INCOME_TAX_TYPE.
PO_LINE_LOCATIONS (PO Shipments)
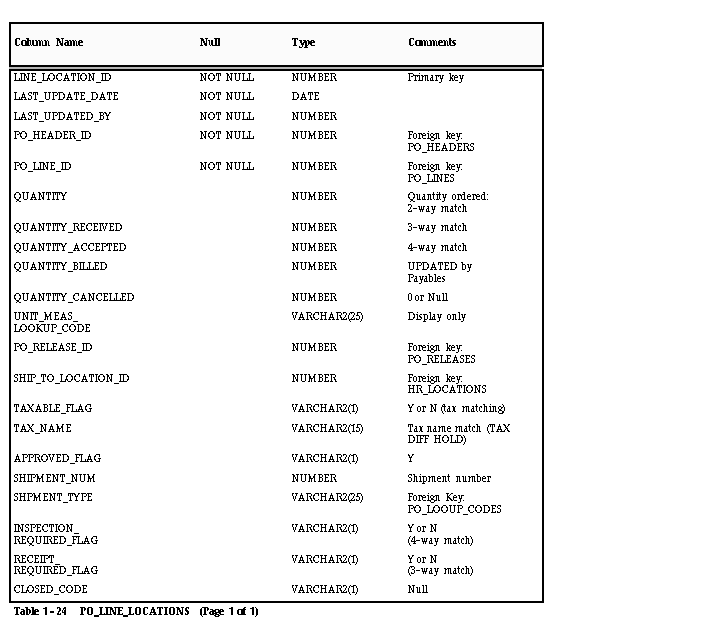
QUANTITY
Enter the quantity of goods ordered for the purchase order shipment. Payables uses this amount to match against if you are using 2-way matching. Payables verifies that this quantity matches the invoice quantity within defined tolerance levels and places the invoice on hold if it doesn’t match. In addition, if the quantity of the invoice is greater than the shipment quantity, your Payables warns you during invoice entry that the match will result in an overbill.
QUANTITY_RECEIVED/QUANTITY_ACCEPTED
Enter the quantity of goods received/accepted if you are using 3-way/4-way matching. Payables verifies that the quantity matches the invoice quantity within defined tolerance levels and places the invoice on hold if it doesn’t match.
QUANTITY_BILLED
Do not enter a value in this column, unless you have already matched an invoice to this purchase order shipment. When a match successfully completes (invoice is approved), Payables updates this column with the quantity you specified during matching.
QUANTITY_CANCELLED
Only enter a value in this column if you have cancelled a portion of the purchase order shipment in your non-Oracle purchasing system. The amount you enter reduces the amount that Payables considers to be the outstanding quantity ordered. Payables displays a warning if you try to match to a shipment which has been cancelled. When you cancel a shipment, Oracle Purchasing sets the PO_LINE_LOCATIONS.QUANTITY_CANCELLED to:
- QUANTITY – QUANTITY_RECEIVED if receipt is required
- QUANTITY – QUANTITY_BILLED if receipt is not required.
Attention: Approval does all quantity checks assuming the QUANTITY is the actual QUANTITY minus the QUANTITY_CANCELLED.
UNIT_MEAS_LOOKUP_CODE
Payables displays this value in the matching zones, but does not validate the column. You can enter any value into this column; however, you should use the same value that you use in your non-Oracle purchasing system.
TAXABLE_FLAG
Enter Y or N to indicate the purchase order shipment is subject to tax. If you enter Y, enter a value in the TAX_NAME column. During Approval, Payables verifies that the tax name for the purchase order shipment matches the tax name on the invoice and places a Tax Difference hold on the invoice if the tax names don’t match.
TAX_NAME
Enter the tax name used to verify that the tax names on the invoice and purchase order shipment match. You do not need to enter a value if you enter N in the TAXABLE_FLAG column. You can obtain a list of valid tax names from AP_TAX_CODES.NAME.
TYPE_LOOKUP_CODE
Enter BLANKET, STANDARD, or SCHEDULED (Lookup Type: SHIPMENT TYPE) to identify the type of purchase order shipment.
CLOSED_CODE
Do not enter a value in this column if you want to match an invoice to this purchase order shipment. If you enter the values CLOSED, FINALLY CLOSED, or CLOSED FOR INVOICE in the column, Payables warns you that you are matching to a closed purchase order.
PO_DISTRIBUTIONS (Account distribution)
Payables uses a view (PO_DISTRIBUTIONS_AP_V) to this table to perform purchase order distribution matching. 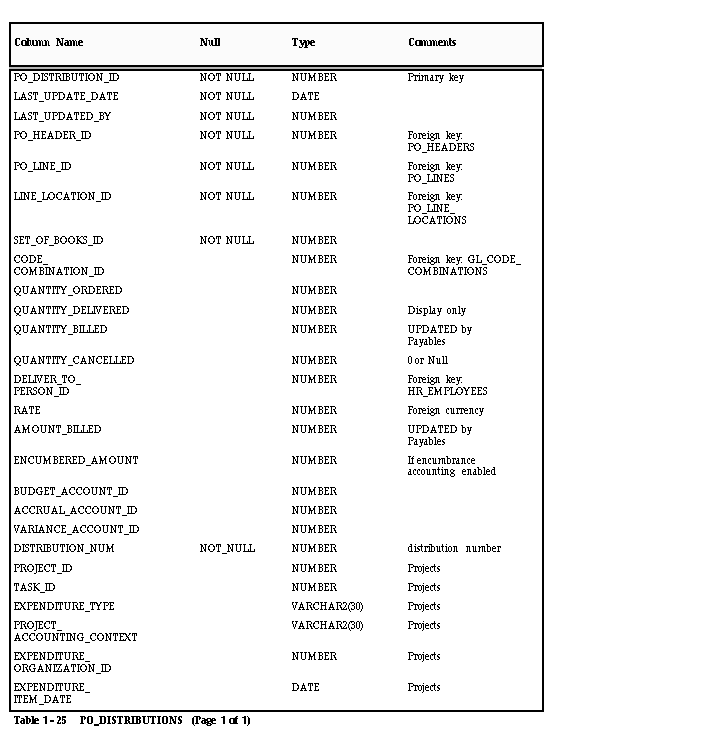
SET_OF_BOOKS_ID
Enter the set of books ID for your purchase order distribution. The ID you enter must be for the set of books you define in the Set of Books window.
CODE_COMBINATION_ID
Enter the Accounting Flexfield ID for the expense account you want to charge for the goods on the purchase order distribution.
QUANTITY_ORDERED
Enter the amount of goods charged to the Accounting Flexfield for this purchase order distribution.
Attention: NOTE: Payables does not validate the following, but assumes it to be true:
Total of PO_DISTRIBUTIONS.QUANTITY_ORDERED for one PO_LINE_LOCATION_ID = PO_LINES_LOCATIONS.QUANTITY (for the same ID).
Payables sometimes prorates the PO_DISTRIBUTION.QUANTITY_ORDERED using the PO_LINES_LOCATIONS.QUANTITY as the total.
BUDGET_ACCOUNT_ID/ACCRUAL_ACCOUNT_ID/ VARIANCE_ACCOUNT_ID
Enter the same Accounting Flexfield ID you entered for the CODE_COMBINATION_ID. Payables allows you to record budget, accrual, and variance (price and exchange rate) amounts for your purchase order distributions, but requires you to charge these amounts to the same expense account for the distribution.
QUANTITY_BILLED
Do not enter a value in this column, unless you have already matched an invoice distribution to this purchase order distribution. When a match successfully completes (invoice is approved), Payables updates this column with the quantity you specified during matching.
QUANTITY_CANCELLED
Enter a value in this column only if you have cancelled a portion of the purchase order distribution in your non-Oracle purchasing system. The amount you enter reduces the amount that Payables considers to be the outstanding quantity ordered. Payables displays a warning if you try to match to a shipment which has been cancelled.
Attention: Approval does all quantity checks assuming the quantity for the distribution is QUANTITY_ORDERED minus QUANTITY_CANCELLED.
AMOUNT_BILLED
Do not enter a value in this column, unless you have already matched an invoice to this purchase order shipment. When a match successfully completes (invoice is approved), Payables updates this column with the amount of the quantity you specified during matching multiplied by the unit price.
Oracle Projects Columns
Enter project information from Oracle Projects if you want to associate the invoice distribution (created through matching) with a project in Oracle Projects. Payables transfers the information into the AP_INVOICE_DISTRIBUTIONS table and uses it to create the default Accounting Flexfield for the invoice distribution.
Matching to Purchase Orders
Perform the following steps to match invoices to purchase order information from your non-Oracle purchasing system:
Create Flat File with Purchasing Information
To load invoice information into Payables via SQL*Loader, first create a program that produces a flat file containing the information from your non-Oracle purchasing system for the purchase orders you want to match to invoices.
Load Information into Purchasing Tables
Use SQL*Loader to load the required information into the purchasing tables. You will need to create a SQL*Loader control file to format the information you want to load. The file you write will vary greatly depending on the nature and format of the flat file you use. Your control file must populate the purchasing tables as indicated in the previous table descriptions. See also: SQL*Loader (ORACLE8 Server Utilities Guide).
Enter Invoices
You match invoices to purchase order shipments during invoice entry. This online function links an invoice in the database to one or more purchase order shipments you choose. You cannot pay or post an invoice until Approval approves the invoice. You can match any type of invoice to a purchase order, including credit and debit memos.
Match to Purchase Order Shipments and distributions
When you match during invoice entry, you indicate whether you want to match to the purchase order shipment or to specific invoice distributions. You then choose the shipment or distribution you want to match to, and the quantity and price you are matching. Then Payables performs the following for each matched shipment:
- Update QUANTITY_BILLED and AMOUNT_BILLED in PO_DISTRIBUTIONS
- Update QUANTITY_BILLED in PO_LINE_LOCATIONS
- Create one or more AP_INVOICE_DISTRIBUTIONS which record the QUANTITY_INVOICED, UNIT_PRICE, and PO_DISTRIBUTION_ID, in addition to other payables information.
Match to Credit and Debit Memos
Payables lets you enter a credit or debit memo (with a negative amount) and match to a purchase order. You would enter a negative quantity in the Quantity Invoiced field in the Purchase Order Shipment Match zone, thereby matching this credit invoice to one or no purchase order shipment lines. Payables then decreases the quantity billed against the purchase order shipment line(s). When you match a credit invoice to a purchase order shipment line, Payables:
- Reopens closed shipment lines (sets PO_LINE_LOCATIONS.CLOSED_CODE to NULL)
- Updates PO_LINE_LOCATIONS.QUANTITY_BILLED
- Updates PO_DISTRIBUTIONS.QUANTITY_BILLED
Attention: Payables does not update any receiving information. You must install Oracle Purchasing if you want to enter or update receiving information for a purchase order
Close a Purchase Order Shipment
Invoice entry closes a purchase order shipment (sets CLOSED_CODE in PO_LINE_LOCATIONS to ‘CLOSED’) when:
- QUANTITY_BILLED equals or exceeds QUANTITY_ORDERED (two-way matching), or
- QUANTITY_ORDERED is less than or equal to QUANTITY_RECEIVED and QUANTITY_RECEIVED is less than or equal to QUANTITY_BILLED
Final Close
Payables does not support finally closing a purchase order if you do not install Oracle Purchasing with Payables. Final close allows you to match an invoice to a purchase order and permanently close the purchase order when you approve the invoice.
Online Review of Purchasing Information
Without an Oracle Purchasing application, Payables does not allow you to review purchasing information, such as purchase order header and line information, online in the Invoice Workbench.
Using Approval
Approval is the Payables feature that performs two-, three-, or four-way matching. An invoice must pass Approval before you can pay or post the invoice. Approval reviews each invoice and places one or more matching holds on the invoice if the invoice does not meet your matching criteria. It also releases any existing matching holds if you adjust your invoice or purchase order to meet your matching criteria and current information on order, receipt and acceptance prices and quantities. You must submit Approval for all invoices, not just matched invoices, since it also checks for distribution variances, tax variances, and exchange rate information. You can submit Approval online for an invoice or in batch for a group of invoices. See also:
Approval.
2-way, 3-way, and 4-way Matching
When you match to a purchase order, Payables automatically checks that the total of PO_DISTRIBUTIONS.QUANTITY_ORDERED = AP_INVOICE_DISTRIBUTIONS.QUANTITY_INVOICED (2-way matching). Payables only checks QUANTITY_RECEIVED (3-way matching) if the RECEIPT_REQUIRED_FLAG is set to Y and only checks QUANTITY_ACCEPTED (4-way matching) if the INSPECTION_REQUIRED_FLAG is set to Y.
Tax Matching
Payables only checks for tax name matching if the Payables option Validate PO Tax Name is enabled and the invoice has distributions with tax names.
Matching Tolerance
You can define percentage and amount tolerances for Matching quantities and price. Payables places a matching hold on an invoice only if the invoice quantity or price is greater than the purchasing quantity or price by more than your tolerance.
Matching Holds
When you submit Approval, Payables places a matching hold on a matched invoice (by inserting one or more rows in AP_HOLDS, one row for each type of hold for each invoice distribution) if:
- QUANTITY_BILLED > QUANTITY in PO_LINE_LOCATIONS (QTY ORD Hold)
- UNIT_PRICE in AP_INVOICE_DISTRIBUTIONS > PRICE_OVERRIDE in PO_LINE_LOCATIONS (PRICE Hold)
- QUANTITY_BILLED > QUANTITY_RECEIVED in PO_LINE_LOCATIONS (QTY REC Hold)
- QUANTITY_BILLED > QUANTITY_ACCEPTED in PO_LINE_LOCATIONS (QUALITY Hold)
- TAXABLE_FLAG = NO in PO_LINE_LOCATIONS, but there IS tax recorded on the invoice (TAX DIFFERENCE Hold)
- TAX_NAME in PO_LINE_LOCATIONS is not equal to VAT_CODE in AP_INVOICE_DISTRIBUTIONS (TAX DIFFERENCE Hold)
Using Encumbrance Accounting with Purchasing
Payables supports using encumbrance accounting with a non-Oracle purchasing system. To use encumbrance accounting, however, you must initially record the encumbered amount for the purchase order to which you want to match an invoice. Then, when Approval approves the invoice, if there is a variance between the invoice and its matched purchase order within the tolerances you define, Payables automatically creates an encumbrance journal entry for the amount of the variance. Payables always creates encumbrance journal entries in detail.
Attention: Approval uses the Payables table, AP_TRANSFER_ENCUMBRANCE, if you enable encumbrance accounting. Payables never drops this table, but deletes the appropriate lines from this table at the beginning of the program each time you submit Approval.
With an Oracle Purchasing application installed, Payables allows you to record these variance encumbrance journal entries to a separate variance account. With a non-Oracle purchasing system, Payables requires you to record the variance amount to the same Accounting Flexfield as the expense Accounting Flexfield for the purchase order distribution.
When you post the invoice to your general ledger, Payables relieves both the original encumbrance journal entries that you created when you encumbered the purchase order and the encumbrance journal entries it automatically created for the variance. Payables then creates actual journal entries for your invoice transaction. Your variance encumbrance journal entries and your actual journal entries update your account balances only when you post the journal entries in your general ledger.
Budgetary Control
The budgetary control feature does not use purchasing information unless you install Oracle Purchasing.
Encumbrance Entries in Payables
If you enable Budgetary Control for a set of books in Oracle General Ledger, you can reserve funds, or encumber them, when you expect an expense so you can avoid overspending a budget and to predict cash outflow. If you enable the PO Encumbrance Financials option, Purchasing and Payables create encumbrances and unencumbrances against the budgets you define in General Ledger. The following equation always holds true:
Funds Available = Budget – Actuals – Encumbrances
The encumbrances Purchasing and Payables create depends on whether the invoice is purchase order matched, and what accrual method you use in Purchasing:
- Unmatched Invoice: If you enable the PO Encumbrance Financials option and you enter an unmatched invoice, Payables creates an encumbrance for the expense during Approval, and reverses this encumbrance during posting.
- Matched Invoice, Receipt Accrual: If you use the On Receipt Accrual Method in Purchasing, Purchasing creates an encumbrance for the goods received at the time of receipt, then reverses that encumbrance when it records the actual expense at the time of delivery of goods. When the invoice is matched to a purchase order and approved in Payables, it is not necessary for Payables to record an encumbrance for the expense. However, Payables will create an encumbrance for an invoice price variance or exchange rate variance, if they exist. Payables does not currently create encumbrances for Quantity variances when you accrue on receipt.
- Matched Invoice, Period End: If you use the Period End Accrual method for your expense items in Purchasing, Purchasing creates an encumbrance for the goods received at the time of delivery. When the invoice is matched to a purchase order and approved in Payables, it is not necessary for Payables to record an encumbrance for the expense. However, Payables will create an encumbrance for a quantity variance, invoice price variance, or exchange rate variance, if any exist.
Payables reverses all remaining encumbrances for an invoice during Posting, when it records the actual invoice expense. The chart below shows when Payables creates encumbrance entries under the two different Accrual Methods.
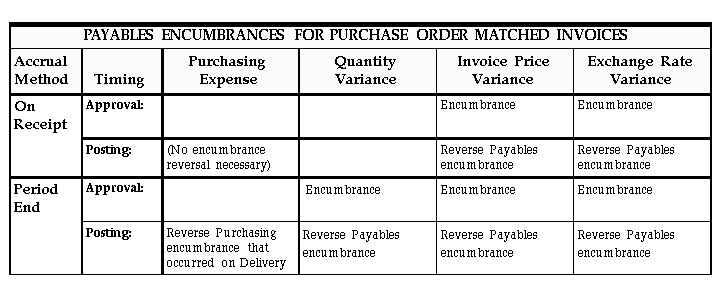
Encumbrance with Combined Basis Accounting
If you use the combined basis accounting method, Payables posts encumbrance entries to your primary, accrual set of books only.
Encumbrance with Cash Basis Accounting
If you use the cash basis accounting method, Payables relieves encumbrance entries when you post payments. Payables prorates your encumbrance reversal based on the amount of your invoice payment.
Purging Purchasing Information
Payables does not allow you to purge purchasing information if you do not have an Oracle Purchasing application installed. When you match an invoice to a purchase order from a non-Oracle purchasing system, you will not be able to purge the invoice because Payables requires that all objects, including matched purchase orders, associated with an invoice must be purgeable before you can purge the invoice.
Select Copy From from the tools menu (or press Alt+T). We are going to copy the attributes from the Finished Good template:












Recent Comments