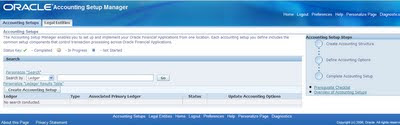
Accounting setup in Oracle General Ledger – R12
Operating Units,
Subledger Accounting,
Intercompany and Intracompany Balancing, and
Reporting Currencies
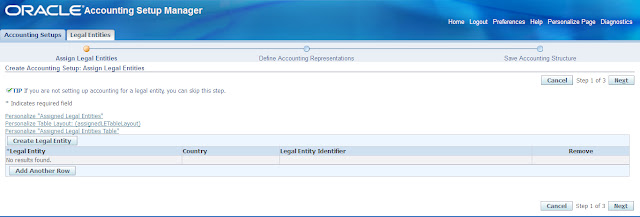
If legal entities are involved, we need to define separate accounting setup for each legal entity, which require it’s own primary ledger. So ledgers have to be defined for each legal entity separately.
The need for other legal entity depends on Chart of Accounts, calendar, Currency, Accounting Method and Ledger processing options. If a legal entity requires any one of the above attributes to be different, a separate primary ledger is required.
Chart of accounts refers to the number of segments that a Chart of accounts structure consistes of.
Calendar refers to the type of accounting calendar that a legal entity uses. Ex: Monthly or Quarterly Calendar.
Currency refers to the primary currency that a legal entity belongs to.
Accounting Method refers to the subledger accounting methods based on the different accounting standards that a legal entity operates.
Ledger Options refers to the options that control how journals and transactiones are processed for a ledger.
Ex: Journal approval, Suspense account, Average balances, Intracompany balancing option, etc.
If we assign Legal entities to the accounting structure, we must assign specific balancing segment values to legal entities to identify and secure transactions by legal entity.
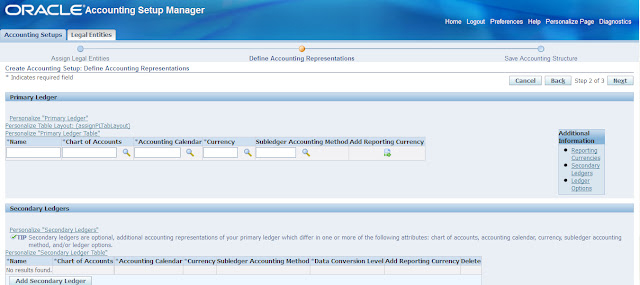
Primary Ledgers are mandatory. We need to define the primary ledger for each legal entity and accounting setup.
Chart of Accounts,
Currency,
Calendar,
Accounting Convention
Secondary ledgers can be maintained at different levels such as:
Subledger level
Journal level
Balance level
Adjustments
Reporting currencies have to be assigned when you want diferent currency representation to primary or secondary ledgers. Reporting currencies must share same chart of accounts,calendar,accounting method and ledger processing options as their source ledger. Reporting currencies can be assigned at different levels.
Subledger level
Journal level
Balance level
We can not use subledger level reporting currencies for secondary ledgers.

Quite informative post, thanks for posting it.
accounts for small business