This article lists the Order to Cash Flow in R12, with technical flow of data as taught in our FocusThread trainings.
1. Order Entry
This is first stage, When the order is entered in the system, it creates a record in order headers and Order Lines table.
Enter header details: Once you enter details on the order header and save it or move it to lines, record goes to one table oe_order_headers_all flow_status_code = ENTERED, booked_flag = N), Primary key=HEADER_ID
No record exist in any other table for this order till now.
Enter Line details for this order: Enter different item numbers, quantity and other details in line tab. When the record gets saved, it goes to one table. Order header details will be linked with line details by order HEADER_ID. oe_order_lines_all (flow_status_code = ENTERED, booked_flag = N, open_flag = Y) Primary key= LINE_ID
2.Order Booking
This is next stage, when Order is booked then the Flow status changed from Entered to Booked. At this stage, these below table get affected.
oe_order_headers_alL (flow_status_code as BOOKED, booked_flag updated to Y)
oe_order_lines_all (flow_status_code as AWAITING_SHIPPING, booked_flag updated Y)
wsh_delivery_details (DELIVERY_DETAIL_ID is assigned here, released_status ‘R’ ready to release, LINE_ID comes as SOURCE_LINE_ID)
wsh_delivery_assignments (DELIVERY_ASSIGNMENT_ID is assigned for DELIVERY_DETAIL_ID present in wsh_delivery_details, DELIVERY_ID remains blank till this stage)
*In shipping transaction form order status remains “Ready to Release”.
At the same time, Demand interface program runs in background And insert into inventory tables mtl_demand, here LINE_ID come as a reference in DEMAND_SOURCE_LINE
3. Reservation
This step is required for doing reservations SCHEDULE ORDER PROGRAM runs in the background and quantities are reserved. Once this program get successfully get completed, the mtl_demand and mtl_reservations table get updated. LINE_ID gets updated in DEMAND_SOURCE_LINE_ID in both the tables.
4. Pick Release
Pick Release is the process of putting reservation on on-hand quantity available in the inventory and pick them for particular sales order.
Pick release can be done from ‘Release Sales Order’ form or ‘Pick release SRS’ program can be scheduled in background. In both of these cases all lines of the order gets pick released depending on the Picking rule used. If specific line/s needs to be pick release it can be done from ‘Shipping Transaction form. For this case Pick Release is done from ‘Release Sales Order’ form with Pick Confirm=NO.
Once pick release is done these are the tables get affected:
If step 3 is not done then MTL_RESERVATIONS gets updated now.
wsh_new_deliveries (one record gets inserted with SOURCE_HEADER_ID= order header ID, status_code=OP =>open)
wsh_delivery_assignments (DELIVERY_ID gets assigned which comes from wsh_new_deliveries)
wsh_delivery_details (released_status ‘S’ ‘submitted for release’)
MTL_TXN_REQUEST_HEADERS
MTL_TXN_REQUEST_LINES (LINE_ID goes as TXN_SOURCE_LINE_ID)
(move order tables. Here request is generated to move item from Source (RM or FG) sub-inventory to staging sub-inventory)
Mtl_material_transactions_temp (link to above tables through move_order_header_id/line_id, this table holds the record temporally)
MTL_SERIAL_NUMBERS_TEMP (if item is serial controlled at receipt then record goes in this table)
MTL_SERIAL_NUMBERS (enter value in GROUP_MARK_ID )
*In shipping transaction form order status remains “Released to Warehouse” and all the material still remains in source sub-inventory. We need to do Move Order Transaction for this order. Till this no material transaction has been posted to MTL_MATERIAL_TRANSACTIONS
5.Pick Confirm/ Move Order Transaction
Items are transferred from source sub-inventory to staging Sub-inventory. Here material transaction occurs.
Order line status becomes ‘Picked’ on Sales Order and ‘Staged/Pick Confirmed’ on Shipping Transaction Form.
MTL_MATERIAL_TRANSACTIONS_TEMP (Record gets deleted from here and gets posted to MTL_MATERIAL_TRANSACTIONS)
oe_order_lines_all (flow_status_code ‘PICKED’ )
MTL_MATERIAL_TRANSACTIONS (LINE_ID goes as TRX_SOURCE_LINE_ID)
mtl_transaction_accounts
wsh_delivery_details (released_status becomes ‘Y’ => ‘Released’ )
wsh_delivery_assignments
MTL_ONHAND_QUANTITIES
MTL_SERIAL_NUMBERS_TEMP (record gets inserted after putting details for the item which are serial controlled at ‘Sales order issue’)
MTL_SERIAL_NUMBERS (record gets inserted after putting details for the item which are serial controlled at ‘Sales order issue’)
* This step can be eliminated if we set Pick Confirm=YES at the time of Pick Release
6.Ship Confirm
Here ship confirm interface program runs in background. Data removed from wsh_new_deliveries.
The items on the delivery gets shipped to customer at this stage.
oe_order_lines_all (flow_status_code ‘shipped’)
wsh_delivery_details (released_status ‘C’ ‘Shipped’, SERIAL_NUMBER if quantity is ONE)
WSH_SERIAL_NUMBERS (records gets inserted with the DELIVERY_DETAIL_ID reference, only in case of shipped quantity is two or more)
mtl_transaction_interface
mtl_material_TRANSACTIONS (linked through Transaction source header id)
mtl_transaction_accounts
Data deleted from mtl_demand, MTL_reservations
Item deducted from MTL_ONHAND_QUANTITIES
MTL_SERIAL_NUMBERS_TEMP (records gets deleted from this table)
MTL_SERIAL_NUMBERS (Serial number stauts gets updated CURRENT_STATUS=4 , ‘Issued out of store’)
7.Enter Invoice
After shipping the order the order lines gets eligible to get transfered to RA_INTERFACE_LINES_ALL. Workflow background engine picks those records and post it to RA_INTERFACE_LINES_ALL. This is also called Receivables interface, that mean information moved to accounting area for invoicing details. Invoicing workflow activity transfers shipped item information to Oracle Receivables. At the same time records also goes in the table RA_INTERFACE_SALESCREDITS_ALL which hold details of sales credit for the particular order.
ra_interface_lines_all (interface table into which the data is transferred from order management) Then Autoinvoice program imports data from this table which get affected into this stage are receivables base table. At the same time records goes in
ra_customer_trx_all (cust_trx_id is primary key to link it to trx_lines table and trx_number is the invoice number)
ra_customer_trx_lines_all (line_attribute_1 and line_attribute_6 are linked to order number and line_id of the orders)
8.Complete Line
In this stage order line level table get updated with Flow status and open flag.
oe_order_lines_all (flow_status_code ‘shipped’, open_flag “N”)
9.Close Order
This is last step of Order Processing. In this stage only oe_order_lines_all table get updated. These are the table get affected in this step.
oe_order_lines_all (flow_status_code ‘closed’, open_flag “N”)
oe_order_HEADERS_all
In this stage order line level table get updated with Flow status and open flag.
oe_order_lines_all (flow_status_code ‘shipped’, open_flag “N”)
9.Close Order
This is last step of Order Processing. In this stage only oe_order_lines_all table get updated. These are the table get affected in this step.
oe_order_lines_all (flow_status_code ‘closed’, open_flag “N”)
oe_order_HEADERS_all

AR Invoices with Rules
Invoices with Rules
Accounting Rules
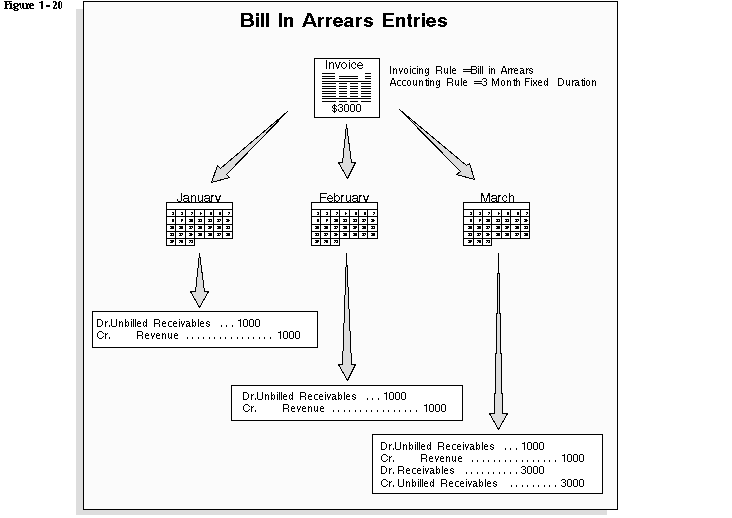
Use accounting rules to determine revenue recognition schedules for your invoice lines. You can assign a different accounting rule to each invoice line. Accounting rules let you specify the number of periods and the percentage of the total revenue to recognize in each period. You can also specify whether the accounting rules are of Fixed or Variable Duration. Accounting rules of Fixed Duration span a predefined number of periods. Accouning rules of Variable Duration let you define the number of periods during invoice entry.
Invoicing Rules
Use invoicing rules to determine when to recognize your receivable for invoices that span more than one accounting period. You can only assign one invoicing rule to an invoice. Receivables provides the following invoicing rules:
Account Sets
Account sets are templates used to create revenue and offset accounting distributions for individual invoice lines with accounting rules. These account sets enable you to split revenue for a line over one or more revenue or offset accounts. You can change account sets from period to period to meet your business requirements. For example, you have an invoice with revenue that you want to recognize over a twelve month period, and the cost center of one of the accounts changes during the twelve months. You can update the account sets to the new cost center account for all of the revenue distributions still to be created. AutoAccounting creates the initial revenue and offset account sets for your invoice.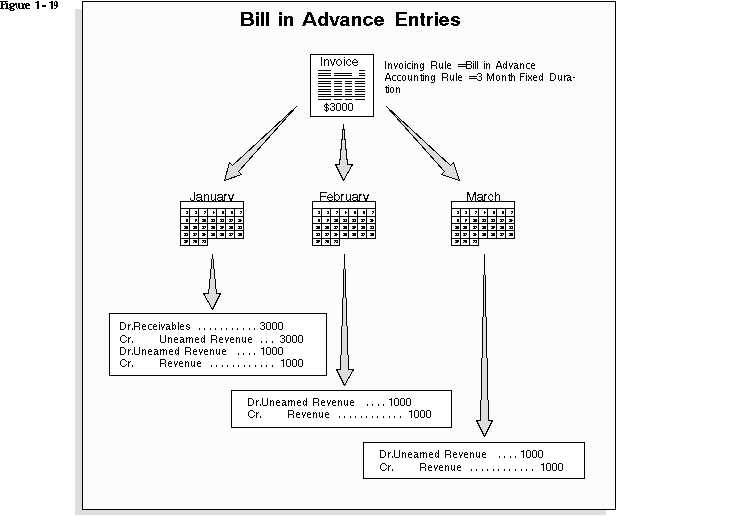
Revenue Recognition
The Revenue Recognition program identifies all transactions with rules within a given period or range of GL dates and creates the revenue distributions for those transactions. The distributions are created for the current period only, using the rules associated with the transactions.
Share this:
Order Management (JSW) Basic Setup steps
Share this:
ORDER MANAGEMENT Interview Questions
Q: What are the Process Constraints?
A: Processing Constraints allow Order Management users the ability to control changes to sales orders, at all stages of its order or line workflows to avoid data inconsistencies and audit problems.
Q: What is a Pick Slip Report?
A: Pick slip is a shipping document that the pickers use to locate items in the warehouse/ inventory to ship for an order.
Q: At what stage an order cannot be cancelled?
A: If the order is Pick Confirmed, it cannot be cancelled.
Q: When the order import program is run it validates and the errors occurred can be seen in?
A: Order Management Responsibility >Orders, Returns : Import Orders> Corrections
Q: What is the difference between purchase order (PO) and sales order?
A: Purchase Order: The document which is created and sent to supplier when we need to purchase something. (Buying)
Sales Order: The document which is created when customer places an order to buy something. (Selling)
Q: What are primary and secondary price lists?
A: Price list contains information on items and its prices. The pricing engine uses secondary price lists when it cannot determine the price for an item using the price list assigned to an order.
Q: Name some tables in shipping/order/move order/inventory?
A: WSH_DELIVERY_DETAILS,WSH_NEW_DELIVERIES, OE_ORDER_HEADERS_ALL, OE_ORDER_LINES_ALL, MTL_SYTEM_ITEMS_B, MTL_MATERIAL_TRANSACTIONS
Q: How is move order generated?
A: When the order is pick released.
Q: What is ONT stands for?
A: ORDER MANAGEMENT
Q: What does Back ordered mean in OM?
A: An unfulfilled customer order due to non-existence of the ordered items in the Inventory.
Q: What are picking rules?
A: A user-defined set of criteria to define the priorities Order Management uses when picking items out of finished goods inventory to ship to a customer. Picking rules are defined in Oracle Inventory.
Q: What is drop ship in OM?
A: A method of fulfilling sales orders by selling products without handling, stocking,or delivering them. The selling company buys a product from a supplier and has the supplier ship the product directly to customers.
Q: What are Defaulting Rules?
A: While creating the order,you can define defaulting rules so that the default values of the fields pop up automatically instead of typing all information.
Q: What are validation templates?
A: A validation template names a condition and defines the semantics of how to validate that condition. Validation templates can be used in the processing constraints framework to specify the constraining conditions for a given constraint.
Q: What are different Order Types?
A: Order Only, Mixed, RMA
Q: Explain the Order Cycle?
A: Book the order
Pick Release
Pick Confirm
Ship Confirm
Close the order
Q: What is packing slip?
A: An external shipping document that is sent along with a shipment itemizing in detail the contents of that shipment.
Q: When an order cannot be deleted?
A: Order cannot be delted if the Order is Pick Confirmed.
Q: What is pick slip?
A: Pick slip is a shipping document that the pickers use to locate items in the warehouse/ inventory to ship for an order.
Q: What is Drop shipment?
A: Drop Shipment is a process where the customer places a purchase order on a company and this company instructs its supplier to directly ship the items to the customer.
Share this:
Tables effected in the OM process
oe_order_lines_all,
oe_order_holds_all,
oe_transaction_types_tl,
cs_customer_product_statuses,
cs_customer_products_all ,
wsh_delevery_details
For Deemed Products:-
MTL_UNIT_TRANSACTIONS,
MTL_MATERIAL_TRANSACTIONS
oe_order_headers_all,
oe_order_holds_all,
oe_order_sources,
oe_transaction_types_all,
oe_sales_credits,
oe_order_lines_all,
oe_order_lines_history,
oe_reservtns_iface_all,
wsh_delivey_details
Share this:
Order to Cash – Technical Flow in R12
1. Order Entry
This is first stage, When the order is entered in the system, it creates a record in order headers and Order Lines table.
Enter header details: Once you enter details on the order header and save it or move it to lines, record goes to one table oe_order_headers_all flow_status_code = ENTERED, booked_flag = N), Primary key=HEADER_ID
No record exist in any other table for this order till now.
Enter Line details for this order: Enter different item numbers, quantity and other details in line tab. When the record gets saved, it goes to one table. Order header details will be linked with line details by order HEADER_ID. oe_order_lines_all (flow_status_code = ENTERED, booked_flag = N, open_flag = Y) Primary key= LINE_ID
2.Order Booking
This is next stage, when Order is booked then the Flow status changed from Entered to Booked. At this stage, these below table get affected.
oe_order_headers_alL (flow_status_code as BOOKED, booked_flag updated to Y)
oe_order_lines_all (flow_status_code as AWAITING_SHIPPING, booked_flag updated Y)
wsh_delivery_details (DELIVERY_DETAIL_ID is assigned here, released_status ‘R’ ready to release, LINE_ID comes as SOURCE_LINE_ID)
wsh_delivery_assignments (DELIVERY_ASSIGNMENT_ID is assigned for DELIVERY_DETAIL_ID present in wsh_delivery_details, DELIVERY_ID remains blank till this stage)
*In shipping transaction form order status remains “Ready to Release”.
At the same time, Demand interface program runs in background And insert into inventory tables mtl_demand, here LINE_ID come as a reference in DEMAND_SOURCE_LINE
3. Reservation
This step is required for doing reservations SCHEDULE ORDER PROGRAM runs in the background and quantities are reserved. Once this program get successfully get completed, the mtl_demand and mtl_reservations table get updated. LINE_ID gets updated in DEMAND_SOURCE_LINE_ID in both the tables.
4. Pick Release
Pick Release is the process of putting reservation on on-hand quantity available in the inventory and pick them for particular sales order.
Pick release can be done from ‘Release Sales Order’ form or ‘Pick release SRS’ program can be scheduled in background. In both of these cases all lines of the order gets pick released depending on the Picking rule used. If specific line/s needs to be pick release it can be done from ‘Shipping Transaction form. For this case Pick Release is done from ‘Release Sales Order’ form with Pick Confirm=NO.
Once pick release is done these are the tables get affected:
If step 3 is not done then MTL_RESERVATIONS gets updated now.
wsh_new_deliveries (one record gets inserted with SOURCE_HEADER_ID= order header ID, status_code=OP =>open)
wsh_delivery_assignments (DELIVERY_ID gets assigned which comes from wsh_new_deliveries)
wsh_delivery_details (released_status ‘S’ ‘submitted for release’)
MTL_TXN_REQUEST_HEADERS
MTL_TXN_REQUEST_LINES (LINE_ID goes as TXN_SOURCE_LINE_ID)
(move order tables. Here request is generated to move item from Source (RM or FG) sub-inventory to staging sub-inventory)
Mtl_material_transactions_temp (link to above tables through move_order_header_id/line_id, this table holds the record temporally)
MTL_SERIAL_NUMBERS_TEMP (if item is serial controlled at receipt then record goes in this table)
MTL_SERIAL_NUMBERS (enter value in GROUP_MARK_ID )
*In shipping transaction form order status remains “Released to Warehouse” and all the material still remains in source sub-inventory. We need to do Move Order Transaction for this order. Till this no material transaction has been posted to MTL_MATERIAL_TRANSACTIONS
5.Pick Confirm/ Move Order Transaction
Items are transferred from source sub-inventory to staging Sub-inventory. Here material transaction occurs.
Order line status becomes ‘Picked’ on Sales Order and ‘Staged/Pick Confirmed’ on Shipping Transaction Form.
MTL_MATERIAL_TRANSACTIONS_TEMP (Record gets deleted from here and gets posted to MTL_MATERIAL_TRANSACTIONS)
oe_order_lines_all (flow_status_code ‘PICKED’ )
MTL_MATERIAL_TRANSACTIONS (LINE_ID goes as TRX_SOURCE_LINE_ID)
mtl_transaction_accounts
wsh_delivery_details (released_status becomes ‘Y’ => ‘Released’ )
wsh_delivery_assignments
MTL_ONHAND_QUANTITIES
MTL_SERIAL_NUMBERS_TEMP (record gets inserted after putting details for the item which are serial controlled at ‘Sales order issue’)
MTL_SERIAL_NUMBERS (record gets inserted after putting details for the item which are serial controlled at ‘Sales order issue’)
* This step can be eliminated if we set Pick Confirm=YES at the time of Pick Release
6.Ship Confirm
Here ship confirm interface program runs in background. Data removed from wsh_new_deliveries.
The items on the delivery gets shipped to customer at this stage.
oe_order_lines_all (flow_status_code ‘shipped’)
wsh_delivery_details (released_status ‘C’ ‘Shipped’, SERIAL_NUMBER if quantity is ONE)
WSH_SERIAL_NUMBERS (records gets inserted with the DELIVERY_DETAIL_ID reference, only in case of shipped quantity is two or more)
mtl_transaction_interface
mtl_material_TRANSACTIONS (linked through Transaction source header id)
mtl_transaction_accounts
Data deleted from mtl_demand, MTL_reservations
Item deducted from MTL_ONHAND_QUANTITIES
MTL_SERIAL_NUMBERS_TEMP (records gets deleted from this table)
MTL_SERIAL_NUMBERS (Serial number stauts gets updated CURRENT_STATUS=4 , ‘Issued out of store’)
7.Enter Invoice
After shipping the order the order lines gets eligible to get transfered to RA_INTERFACE_LINES_ALL. Workflow background engine picks those records and post it to RA_INTERFACE_LINES_ALL. This is also called Receivables interface, that mean information moved to accounting area for invoicing details. Invoicing workflow activity transfers shipped item information to Oracle Receivables. At the same time records also goes in the table RA_INTERFACE_SALESCREDITS_ALL which hold details of sales credit for the particular order.
ra_interface_lines_all (interface table into which the data is transferred from order management) Then Autoinvoice program imports data from this table which get affected into this stage are receivables base table. At the same time records goes in
ra_customer_trx_all (cust_trx_id is primary key to link it to trx_lines table and trx_number is the invoice number)
ra_customer_trx_lines_all (line_attribute_1 and line_attribute_6 are linked to order number and line_id of the orders)
8.Complete Line
In this stage order line level table get updated with Flow status and open flag.
oe_order_lines_all (flow_status_code ‘shipped’, open_flag “N”)
9.Close Order
This is last step of Order Processing. In this stage only oe_order_lines_all table get updated. These are the table get affected in this step.
oe_order_lines_all (flow_status_code ‘closed’, open_flag “N”)
oe_order_HEADERS_all
In this stage order line level table get updated with Flow status and open flag.
oe_order_lines_all (flow_status_code ‘shipped’, open_flag “N”)
9.Close Order
This is last step of Order Processing. In this stage only oe_order_lines_all table get updated. These are the table get affected in this step.
oe_order_lines_all (flow_status_code ‘closed’, open_flag “N”)
oe_order_HEADERS_all
Share this: