What is value set in Oracle application AOL?
- Value set is primarily a container for your values, you define your value set such that it can control the types of values that are allowed into the value set (either predefined or nonvalidated). You can specify the format of your values.
- Oracle Application Object Library uses value sets as important components of key flexfields, descriptive flexfields, and Standard Request Submission (value sets for report parameters for your reports that use the Standard Request Submission feature).
When to defining Values for Value Sets?
- After you register your Flexfields & report parameters, if you are using independent or dependent value sets, you can enter values into each corresponding value set using the Segment Values form.
- Values for the Value Sets, we are defining will be kept in the Oracle Application Object Library tables.
How many Format Types the value set have?
- Char
- Date
- DateTime
- Number
- Standard Date
- Standard Date Time
- Time
You should take a note that Date and Date Time value set formats will be obsolete now and are provided for backward compatibility only. For new value sets, use the format types Standard Date and Standard Date Time.
What is Security type in value set?
- By Security Rules window, we can define value security rules for ranges of flexfield and report parameter values.
There are two levels where you must activate Security, the one at value set level and other at individual segment or parameter level. You make Flex field Value Security available for your value set by choosing Hierarchical Security or Non-Hierarchical Security for the Security Type. When you make security available for a value set, all segments and report parameters that use that value set can use security. You then enable security for a particular segment or parameter.
- Choose Hierarchical Security, If you want Security on a parent value to Cascade down to its child value or else you can choose Non-Hierarchical Security.
How many Character Formatting Options have for value set?
- Numbers Only (0 – 9)
- We cannot prevent users from entering a value that contains the radix character.
- Cannot be used in Translatable Independent and Translatable Dependent value sets.
- Uppercase Only(A-Z)
- Here also we cannot use in Translatable Independent and Translatable Dependent value sets.
- Right justify and Zero fill Numbers(001)
- If you have selected Numbers Only (0-9) flag, then it wont allow you to affect this flag.
- We are recommended to use this in Accounting Flex fields.
- Minimum and Maximum Value Range
- Your Minimum/maximum value may not be longer than the maximum size you specify for this value set.
- Once you specify a range of values, you cannot define a new valid value that falls outside this range.
- The Minimum Value and Maximum Value fields can therefore allow you to create a value set with a validation type of None.
How many validation Type does value set have?
There are several validation types that affect the way users enter and use segment or parameter values:
- None (not validated at all)
- Allow users to enter any value.
- Only Format Validations will be done.
- Independent
- Provides a predefined list of values.
- Independent values are stored in an Oracle Application Object Library table.
- Dependent
- Same like Independent Value Set, except the List of Values shown to you will depends on which the Independent value you have selected in the Prior Segment.
- Must define your independent value set before you define the dependent value set that depends on it.
- Advisable to create your independent values first.
- Must create at least one dependent value for each independent value, or else it wont allow you to enter into that segment or field.
- Table
- It use your own application tables as value sets for flex field segments and report parameters instead of the special values tables which Oracle Applications provides.
- You can also use validation tables with other special arguments to make your segments depend on profile options or field values.
- You can use any existing application table, view, or synonym as a validation table.
- If we are using non registered table for your value set, then we have to Create the necessary grants and synonyms to APPS Schema.
- The value column and the defined ID column in the table must return a unique row for a given value or ID.
- If the Hidden Id column is provided the value passed to the report will be Hidden and not the Value column.
- Similarly, when you specify :$FLEX$.Value_Set_Name, your flex field segment or report parameter defaults to always use the hidden ID column to compare with your WHERE clause .
- We can use Special BIND variable such as :$PROFILES$.Option_name, :$FLEX$.Value_set_name, :block.field in the WHERE clause.
- Special
- Special validation value sets allow you to call key flex field user exits to validate a flex field segment or report parameter using a flex field within a flex field mechanism. You can call flex field routines and use a complete flex field as the value passed by this value set.
- Pair
- Pair validation value set allows user to pass a range of concatenated Flex field segments as parameters to a report.
- Translatable Independent & Translatable Dependent
- These value sets are similar to Independent and Dependent value sets except that translated values can be displayed to the user. Translatable Independent and Translatable Dependent value sets allow you to use hidden values and displayed (translated) values in your value sets. In this way your users can see a value in their preferred languages, yet the values will be validated against a hidden value that is not translated.
- We can convert the Independent value set to a Translatable Independent value set, or a Dependent value set to a Translatable Dependent value set. These are the only types of conversions allowed.
Which Oracle table store Value sets and underline information?
- FND_FLEX_VALUE_HIERARCHIES
- FND_FLEX_VALUE_SETS
- FND_ID_FLEX_SEGMENTS
- FND_FLEX_VALUE_NORM_HIERARCHY
- FND_FLEX_HIERARCHIES
- FND_FLEX_VALUE
- FND_FLEX_VALIDATION_EVENTS
- FND_FLEX_VALUE_RULE_LINES
- FND_FLEX_VALUE_RULE
- FND_FLEX_VALUE_RULE_USAGE
- FND_RESPONSIBLITY
- FND_TABLES
- FND_FLEX_VALIDATION_TABLES
Any method to upload flexfield value?
Yes, FNDLOAD is utility which can be used for moving value set across different environment.
Do we have any restriction on value set?
Yes, here are some listed one:
- Table Validated Value Sets
- We cannot use table-validated id value sets for any accounting flexfield or any other key flexfields.
- We cannot use :$FLEX$, :$PROFILES$ in table name, value and id of table validated value sets.
- We cannot use DISTINCT clause in any of the column fields or in the WHERE clause of a table validate value set.
- In an id value set, the value can be non-unique but id should be unique. In a non-id value set, value should be unique.
- We can only use columns selected for the table-validated value set must be of type NUMBER, DATE or VARCHAR2.
- Support for SQL expression in columns of Table Validated value sets will be obsolete in future release.
- Translatable Independent and Translatable Dependent Valuesets
- The Numbers Only and Uppercase Only option cannot be used.
- Must have “Char” format type.
- Special/Pair valuesets
- Special/Pair value sets are user-exit value sets . PL/SQL APIs will not be able to validate them.
Lets now define a simple value set in R12:
Step 1: Go to Application Developer, and select menu /Validation/Set
Create a value set name as COUNTRY_LIST which will contain a list of countries. Make it an independent value set. Format type is CHAR. Save the work.
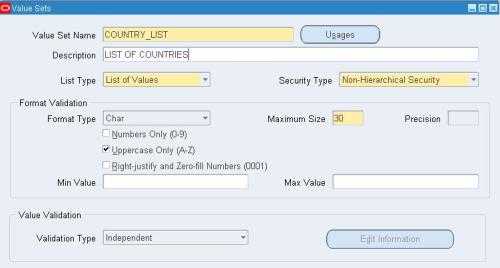
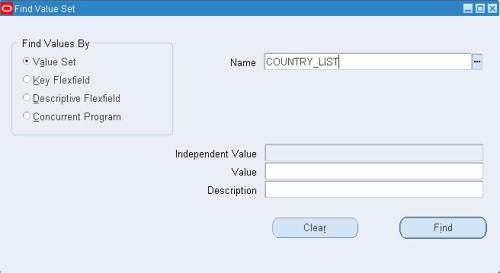
Step 2: Go to Application Developer, and select menu /Validation/Values
The below window will appear. Put the Search Name as COUNTRY_LIST and click Find.
Step 3: Enter the country details in this window. Save the work.
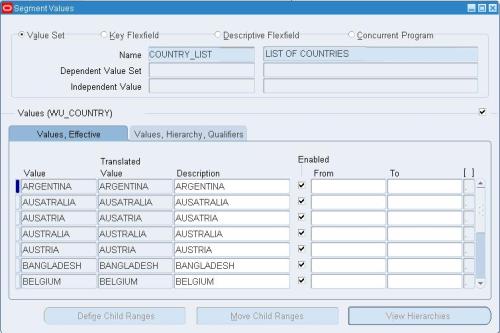
Now the value set is ready to be used in any concurrent program.















Recent Comments