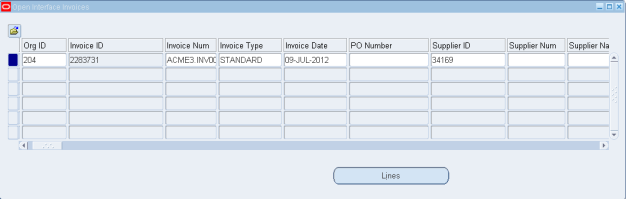
Let’s say Invoices are imported from External Systems – irrespective of the transportation layer / method. Instead of viewing the Interface tables in the back end – say AP_INVOICES_INTERFACE , AP_INVOICE_LINES_INTERFACE, they can be viewed in the front-end.
Responsibility – Payables Manager
Navigation – Invoices – Entry – Open Interface Invoices
Clicking on the above link, opens the below form ..
Open the Query-mode to view the Invoice in the Interface table
Above is the header line. Click on Lines to view the lines information.
This would avoid looking for Invoices by querying in the back-end.
Use E-Business Tax to set up and maintain your transaction tax requirements in all geographic locations where you do business. You can set up tax configurations to include the rules, default values, and other information necessary for each separate tax requirement. At transaction time, E-Business Tax uses your tax configuration to determine the taxes that apply to each transaction and to calculate the tax amounts.
With E-Business Tax, you can:
• Set up and maintain a tax configuration for each tax that you are subject to.
• Set up and maintain records for your legal entities and operating units and the taxes they are subject to.
• Manage the sharing of tax configuration data by the legal entities and operating units in your organization.
• Set up and maintain tax registrations and classifications for your legal establishments and third parties.
• Set up and maintain classifications of the products that you buy and sell.
• Set up and maintain classifications for your transactions.
• Set up and maintain tax rules and default values to manage tax determination and tax recovery on your transactions:
• Set up default values and a minimum number of tax rules for simple tax requirements.
• Set up default values and a comprehensive set of tax rules to manage complex tax requirements.
• Set up and maintain tax-related records for your important transactions.
• Set up and maintain automatic accounting of all tax-related transactions.
• Manage user control of updates and overrides of tax information on transactions.
• Set up and maintain codes for tax reporting purposes.
• Set up and maintain access to third party tax calculation services.
You can use the E-Business Tax Home page to manage access to all parts of the E-Business Tax system for setup and maintenance. The tasks involved in setting up a tax requirement in E-Business Tax fall into three general categories:
1. Setting up transaction taxes.
2. Completing all of the setups and settings related to the processing of taxes on transactions.
3. Setting up tax rules and defaults to manage tax processing.
Steps for E-Business Suite Tax:
Step 1: Create Tax Regime
Step 2: Create Tax
Step 3: Create Tax Status
Step 4: Create Jurisdiction
Step 5: Create Rate
Step 6: Enter Tax Accounts
Step 7: Create Tax Rules (Populate values for all defaults)
Step 8: Make Tax Available for Transaction
Step 9: Test the Tax
Check how the Party/OU has been setup, Tax Manager/Administrator > Parties > Party Tax Profiles
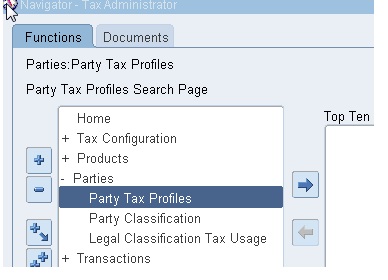
Query for the following:
Party Type: Operating Unit Owning Tax Content
Party Name: Vision Operations (Name of the OU you wish to setup for tax)
Party Type: Operating Unit Owning Tax Content
Party Name: Vision Operations (Name of the OU you wish to setup for tax)
Click Go
Click View Tax Profile
Confirm if ‘Use Subscription of the Legal Entity’ is checked.
Step 1: Create Tax Regime
Navigation : Tax Manager/Administrator > Tax Configuration > Tax Regimes
Navigation : Tax Manager/Administrator > Tax Configuration > Tax Regimes
Click Create to enter a new Tax Regime.
We are going to create a United Kingdom regime.
We are going to create a United Kingdom regime.
Enter the following:
Field Value
Tax Regime Code XXX UK REGIME
Name XXX UK REGIME
Regime Level Country
Country Name United Kingdom
Effective From 10-Jan-2000
Parent Regime Code NULL
Used to Group Regimes Unchecked
Click on Show Controls and Defaults.
Tax Regime Code XXX UK REGIME
Name XXX UK REGIME
Regime Level Country
Country Name United Kingdom
Effective From 10-Jan-2000
Parent Regime Code NULL
Used to Group Regimes Unchecked
Click on Show Controls and Defaults.
Enter settings for Controls and Defaults as follows:
|
Field
|
Value
|
|
Controls:
|
|
|
Allow Tax Recovery
|
Unchecked
|
|
Allow Override and Entry of Inclusive Tax Lines
|
Checked
|
|
Allow Tax Exemptions
|
Checked
|
|
Allow Tax Exceptions
|
Checked
|
|
Defaults:
|
|
|
Tax Currency
|
GBP
|
|
Minimum Accountable Unit
|
0.01
|
|
Rounding Rule
|
Nearest
|
|
Tax Precision
|
2
|
|
Allow Multiple Jurisdictions
|
Unchecked
|
Click Continue
Enter the following information:
|
Field
|
Value
|
|
Party Name
|
Operating Unit
|
|
Party Type
|
Operating Unit Owning Tax Content *
|
|
Configuration for Taxes and Rules
|
Common Configuration
|
|
Configuration for Product Exceptions
|
Common Configuration
|
|
Effective From
|
10-Jan-2000
|
* If ‘Use Subscription of the Legal Entity’ was checked in the prereq step then this would have been entered against the First Party Legal Entity and not the OU
Click on Finish
Ensure you see confirmation message:
Step 2: Create Tax
Navigation: Tax Manager/Administrator > Tax Configuration > Taxes
Navigation: Tax Manager/Administrator > Tax Configuration > Taxes
Click on Create
Enter the following information:
|
Field
|
Value
|
|
Tax Regime Code
|
XXX UK REGIME (From LOV – Regime defined in Step 1)
|
|
Configuration Owner
|
Global Configuration Owner
|
|
Tax Source
|
Create a New Tax
|
|
Tax
|
XXX UK TAX
|
|
Tax Name
|
XXX UK TAX
|
|
Tax Type
|
VAT
|
|
Geography Type
|
Country
|
|
Parent Geography Type
|
Country
|
|
Parent Geography Name
|
United Kingdom
|
|
Set as Offset Tax
|
Unchecked
|
|
Set Tax for Reporting Purposes
|
Unchecked
|
Click on Show Controls and Defaults
Enter the following information:
|
Field
|
Value
|
|
Controls:
|
|
|
Allow Tax Inclusion
|
Unchecked
|
|
Allow Override and Entry of Inclusive Tax Lines
|
Checked
|
|
Allow Tax Rounding Override
|
Checked
|
|
Allow Override for Calculated Tax Lines
|
Checked
|
|
Use Legal Registration Number
|
Unchecked
|
|
Allow Multiple Jurisdictions
|
|
|
Allow Mass Creation of Jurisdictions
|
Checked
|
|
Defaults:
|
Checked
|
|
Allow Tax Rate Rules
|
Checked
|
Click Apply and ensure the confirmation message appears.
Step 3: Create Tax Status
Tax Manager/Administrator > Tax Configuration > Tax Statuses
Click Create
Tax Manager/Administrator > Tax Configuration > Tax Statuses
Click Create
Enter the following information:
|
Field
|
Value
|
|
Tax Regime
|
XXX UK REGIME (From LOV in Step 1)
|
|
Tax
|
XXX UK TAX (From LOV in Step 2)
|
|
Tax Status Code
|
XXX UK STATUS
|
|
Name
|
XXX UK STATUS
|
|
Effective From
|
10-Jan-2000 (Defaults)
|
|
Set as Default Tax Status
|
Checked
|
|
Default Status Effective From
|
10-Jan-2000 *
|
* Does not default and is not required so remember to enter this.
Click Apply
View confirmation message:
View confirmation message:
Step 4: Create Jurisdiction
Tax Manager/Administrator > Tax Configuration > Tax Jurisdiction
Click Create (see above screenshot)
Enter the following information:
|
Field
|
Value
|
|
Tax Jurisdiction Code
|
XXX UK JURISDICTION
|
|
Tax Jurisdiction Name
|
XXX UK JURISDICTION
|
|
Tax Regime Code
|
XXX UK REGIME (From LOV Step 1)
|
|
Tax
|
XXX UK TAX (From LOV Step 2)
|
|
Geography Type
|
COUNTRY
|
|
Effective From
|
10-JAN-2000
|
|
Geography Name
|
United Kingdom
|
|
Default Tax Jurisdiction Settings:
|
|
|
Set as default Tax Jurisdiction
|
Checked
|
|
Default Effective From
|
10-Jan-2000
|
Click Apply
Ensure confirmation message is received.
Ensure confirmation message is received.
Step 5: Create Rate
Tax Manager/Administrator > Tax Configuration > Tax Rates
Click Create (screenshot above)
Enter the following information:
|
Field
|
Value
|
|
Tax Regime Code
|
XXX UK REGIME (From LOV Step 1)
|
|
Configuration Owner
|
Global Configuration Owner
|
|
Tax
|
XXX UK TAX (From LOV Step 2)
|
|
Tax Status Code
|
XXX UK STATUS (From LOV Step 3)
|
|
Tax Jurisdiction Code
|
XXX UK JURISDICTION (From LOV Step 4)
|
|
Tax Rate Code
|
XXX UK RATE
|
|
Rate Type
|
Percentage
|
|
Rate Periods:
|
|
|
Percentage Rate
|
20
|
|
Effective From
|
01-Jan-2000
|
Click on Rate Details button and scroll down
Enter the following:
|
Field
|
Value
|
|
Set as Default Rate
|
Checked
|
|
Default Effective Date
|
01-Jan-2000
|
Click Apply. & Click Apply again.
Ensure confirmation message is received
Step 6: Enter Tax Accounts
Tax Manager/Administrator > Tax Configuration > Taxes
Query XXX UK Tax -> Click Go -> Click Tax Accounts
Tax Manager/Administrator > Tax Configuration > Taxes
Query XXX UK Tax -> Click Go -> Click Tax Accounts
Search for Vision Operations OU and click create
Enter the Operating Unit and populate Tax Expense and Tax Recoverable/Liability accounts.
Click Apply. & Click Apply again Click Apply a third time
Click Apply a third time
Step 7: Create Tax Rules (Populate values for all defaults)
Tax Manager/Administrator > Tax Configuration > Tax Rules
Enter the following:
|
Field
|
Value
|
|
Configuration Owner
|
Global Configuration Owner
|
|
Tax Regime Code
|
XXX UK REGIME
|
|
Tax
|
XXX UK TAX
|
Click Go to search for existing default rule
Click the pencil icon in the Set Default column to change any of the defaults defined
Update the defaults as follows:
|
Field
|
Value
|
|
Determine Place of Supply
|
Ship to, use bill to if ship to is not found
|
|
Determine Tax Applicability
|
Applicable
|
|
Determine Tax Registration
|
STANDARD_TB
|
|
Calculate Tax Amounts
|
STANDARD_TC
|
Step 8: Make Tax Available for Transaction
Tax Manager/Administrator > Tax Configuration > Taxes
Query Tax
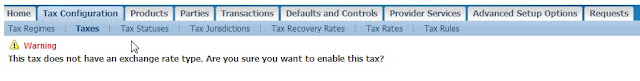
Click on Update Pencil Icon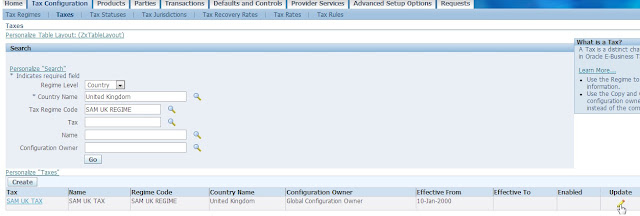
Check the box ‘Make Tax Available for Transactions’
Click Apply
This warning is ok since we know we didn’t enter an exchange rate type.
Click Yes and receive confirmation of changes saved
Step 9: Test the Tax
Payables > Invoices : Entry > Invoices
Enter Invoice for Supplier with a UK Ship-To address Enter Line information
Enter Line information
Ensure the SHIP TO location at the line level contains a UK location (As that is how we determine place of supply)
Click distributions
Enter Invoice distribution
Save
Go back to Invoices and click Calculate Tax
Tax line is created – click on Tax Details
You can see that the SAM UK REGIME has been applied and tax calculated at 20%.
A ledger set is a group of ledgers that share the same chart of accounts and calendar/period type combination. Ledger sets allow you to run processes and reports for multiple ledgers simultaneously.
For example, you can open/close periods for multiple ledgers at once, run recurring journals that update balances for multiple ledgers, or run consolidated financial reports that summarize balances across multiple ledgers in a ledger set. You can group all types of ledgers in a ledger set, such as primary ledger, secondary
ledgers, and reporting currencies (journal and subledger levels), as long as they share the same chart of accounts and calendar/period type combination. The same ledger can belong to multiple ledger sets, and ledger sets can contain other ledger sets.
To define a ledger set:
Navigation: General Ledger –> Setup –> Financials –> Ledger sets.
1. Navigate to the Ledger Set window.
2. Enter a name for the Ledger Set.
3. Enter a Short Name for the ledger set.
4. (Optional) Enter a Description for the ledger set.
5. Choose a Chart of Accounts.
6. Choose a Calendar and Period Type.
7. (Optional) Specify a default ledger. The default ledger automatically defaults in all windows where the Ledger field is required.
Note: A Default Ledger is required for Financial Statement Generator (FSG).
8. (Optional) Select the Enable Security checkbox to secure the Ledger Set definition. If you do not enable security, all users who have access to this definition will be able to use, view, and modify the ledger set definition. If the Assign Access function is available for your responsibility, the Assign Access
button will be enabled once you select the Enable Security checkbox. Choose the Assign Access button to assign the definition to one or more Definition Access Sets with the desired privileges.
9.In the Ledger/Ledger Set column, choose the ledgers and/or ledger sets to be included in the ledger set. Only those ledgers and ledger sets that share the same chart of accounts, calendar, and period type specified for the ledger set definition will be available.
If you use reporting currencies (journal or subledger level), you can choose reporting currencies to be included in the ledger set. Only those reporting currencies that share the same chart of accounts, calendar, and period type specified for the ledger set definition will be available
10. Save your work. The General Ledger Accounting Setup Program will be submitted. Ensure this program completes successfully. Once saved, a ledger set cannot be deleted. You can only add or remove ledgers
and ledger sets from ledger sets.
Note: You must have at least one ledger or ledger set assigned to a ledger set. Before you can begin using the ledgers contained in your ledger set for transaction processing, you must assign the ledger set to the profile option, GL: Data Access Set.
For example, you can open/close periods for multiple ledgers at once, run recurring journals that update balances for multiple ledgers, or run consolidated financial reports that summarize balances across multiple ledgers in a ledger set. You can group all types of ledgers in a ledger set, such as primary ledger, secondary
ledgers, and reporting currencies (journal and subledger levels), as long as they share the same chart of accounts and calendar/period type combination. The same ledger can belong to multiple ledger sets, and ledger sets can contain other ledger sets.
To define a ledger set:
Navigation: General Ledger –> Setup –> Financials –> Ledger sets.
1. Navigate to the Ledger Set window.
2. Enter a name for the Ledger Set.
3. Enter a Short Name for the ledger set.
4. (Optional) Enter a Description for the ledger set.
5. Choose a Chart of Accounts.
6. Choose a Calendar and Period Type.
7. (Optional) Specify a default ledger. The default ledger automatically defaults in all windows where the Ledger field is required.
Note: A Default Ledger is required for Financial Statement Generator (FSG).
8. (Optional) Select the Enable Security checkbox to secure the Ledger Set definition. If you do not enable security, all users who have access to this definition will be able to use, view, and modify the ledger set definition. If the Assign Access function is available for your responsibility, the Assign Access
button will be enabled once you select the Enable Security checkbox. Choose the Assign Access button to assign the definition to one or more Definition Access Sets with the desired privileges.
9.In the Ledger/Ledger Set column, choose the ledgers and/or ledger sets to be included in the ledger set. Only those ledgers and ledger sets that share the same chart of accounts, calendar, and period type specified for the ledger set definition will be available.
If you use reporting currencies (journal or subledger level), you can choose reporting currencies to be included in the ledger set. Only those reporting currencies that share the same chart of accounts, calendar, and period type specified for the ledger set definition will be available
10. Save your work. The General Ledger Accounting Setup Program will be submitted. Ensure this program completes successfully. Once saved, a ledger set cannot be deleted. You can only add or remove ledgers
and ledger sets from ledger sets.
Note: You must have at least one ledger or ledger set assigned to a ledger set. Before you can begin using the ledgers contained in your ledger set for transaction processing, you must assign the ledger set to the profile option, GL: Data Access Set.
Save.
Once you create the ledger set system default created a data access set with the same name of the our Ledger set name.
Navigation: General Ledger –> Setup –> Financials –>Data Access Set
Assign this ledger set to your Responsibility.
Navigation: System administrator –> Profiles –> Systems.
Click on find
Save.
Now we can access one or more Ledgers at a time.
Go to Responsibility: Tax Manager -> Advanced Setup Options -> Tax Lookup Codes
Enter the required code ( ZX_OUTPUT_CLASSIFICATIONS )
Click on Go button
Click on Update Icon
Click on Update Icon
Un check enable check box for which tax code we do not want see AR Module
Click on Apply.
2. If you do not want to see the AR tax codes in AP module
Go to Responsibility: Tax Manager -> Advanced Setup Options -> Tax Lookup Codes
Enter the required code ( ZX_INPUT_CLASSIFICATIONS )
Click on Go button
Click on Update Icon
Click on Update Icon
Un check enable check box for which tax code we do not want see AP Module
Apply .
How to Configure AME in R12 – Assign Roles & Create Grants for User
Oracle Approvals Management (AME) functionality is a self-service web application that allows users to
define rules for administering approvals of various types of transactions. Learn how easy it is to use this
powerful functionality to create complex approval scenarios that meet your unique business requirements.
Case studies of recent successful implementations will be presented for PO, AP and HR. Learn how to
accommodate individual employee signing limits, how to integrate workflow timeout functionality with AME.
Oracle Approvals Management (AME) functionality is a self-service web application that allows users to
define rules for administering approvals of various types of transactions. Learn how easy it is to use this
powerful functionality to create complex approval scenarios that meet your unique business requirements.
Case studies of recent successful implementations will be presented for PO, AP and HR. Learn how to
accommodate individual employee signing limits, how to integrate workflow timeout functionality with AME.
Latest Posts
- R12 – How to Handle NULL for :$FLEX$.VALUE_SET_NAME In Oracle ERPAugust 25, 2023 - 1:20 pm
- R12 – How to Delete Oracle AR TransactionsMarch 22, 2019 - 8:37 pm
- How to Define Custom Key Flexfield (KFF) in R12January 19, 2018 - 5:43 pm
- AutoLock Box Concepts In R12November 10, 2017 - 8:30 am
- R12 – java.sql.SQLException: Invalid column type in OAFSeptember 15, 2017 - 9:39 am
| S | M | T | W | T | F | S |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 |
| 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 |
| 15 | 16 | 17 | 18 | 19 | 20 | 21 |
| 22 | 23 | 24 | 25 | 26 | 27 | 28 |
| 29 | 30 | 31 | ||||







































Recent Comments