-
EBS 12.2 represents our most-groundbreaking release in years (Press Release). It includes new product functionality, new Fusion Middleware and database components, and introduces new tools for installing, configuring, and maintaining E-Business Suite environments:
Hundreds of new features
Includes significant enhancements across the integrated suite of business applications spanning enterprise resource planning, human capital management, and supply chain management. You can find the complete list here:- E-Business Suite 12.2 Release Content Document (Note 1302189.1)
Online PatchingApply EBS patches while users are still entering transactions and using the E-Business Suite. Online Patching uses the Oracle Database’s Edition-Based Redefinition feature and other new technologies to allow the E-Business Suite to be updated while the system is still running. You can learn more about Online Patching via our official documentation and this technical webcast.WebLogic ServerUses Oracle WebLogic Server, which replaces the Oracle Containers for Java (OC4J) application server used in EBS 12.0 and 12.1. You can learn more about how this improves the system administration experience via our official documentation and this technical webcast.Streamlined installation
- Option for installing EBS 12.2 on to existing database servers.
- Capability of installation into existing Real Application Clusters environments.
- Database deployment on Automatic Storage Management (ASM) and other file systems.
Upgrading to EBS 12.2Is there a direct upgrade path from EBS 11i to 12.2?Yes, there is a direct upgrade path from EBS 11.5.10.2 to EBS 12.2. EBS 11.5.10.2 customers do not have to install an intermediary EBS 12 release (such as 12.1.3) before upgrading to EBS 12.2. EBS 11.5.10.2 customers must have applied the minimum baseline patch requirements for Extended Support as described in Patch Requirements for Extended Support of Oracle E-Business Suite Release 11.5.10 (Document 883202.1). Customers on earlier EBS 11i releases (such as 11.5.7) need to be at the 11.5.10.2 level plus the minimum baseline patch requirements for Extended Support before they can upgrade to EBS 12.2.Is there a direct upgrade path from EBS 12.0 to 12.2?Yes, there is a direct upgrade path from EBS 12.0.4 and 12.0.6 to EBS 12.2. EBS 12.0.4 or 12.0.6 customers do not have to install an intermediary EBS 12 release (such as 12.1.3) before upgrading to EBS 12.2. Customers on earlier EBS 12.0 releases (such as 12.0.3) will need to be at the 12.0.4 or 12.0.6 level before they can upgrade to EBS 12.2.Is there a direct upgrade path from EBS 12.1 to 12.2?Yes, there is a direct upgrade path from EBS 12.1.1, 12.1.2, and 12.1.3 to EBS 12.2.How can I prepare for EBS 12.2?- Read the Oracle E-Business Suite 12.2 Technical Planning Guide, First Edition (Note 1585857.1)
More technical references- EBS 12.2 Product Information Center (Note 1581299.1)
- EBS 12.2 Documentation Library (Oracle Technology Network)
Step 1: Create Multi language function in the database
CREATE OR REPLACE PACKAGE APPS.xx_mls_lang AUTHID CURRENT_USERAS FUNCTION get_lang RETURN VARCHAR2;END xx_mls_lang;/CREATE OR REPLACE PACKAGE BODY apps.xx_mls_langAS FUNCTION get_lang RETURN VARCHAR2 IS p_lingo VARCHAR2 (40) := NULL; l_select_statement VARCHAR2 (4000); source_cursor INTEGER; lang_string VARCHAR2 (240) := NULL; l_lang VARCHAR2 (30); l_lang_str VARCHAR2 (500) := NULL; l_base_lang VARCHAR2 (30); l_dummy INTEGER; ret_val NUMBER := NULL; parm_number NUMBER; l_trns_lang_check NUMBER; BEGIN -- Parameter Entry ret_val := fnd_request_info.get_param_number ('Language', parm_number); IF (ret_val = -1) THEN p_lingo := NULL; ELSE p_lingo := fnd_request_info.get_parameter (parm_number); END IF; -- Get Base Language SELECT language_code INTO l_base_lang FROM fnd_languages WHERE installed_flag = 'B'; -- If the user has entered a language/value for the parameter then -- extract it the value IF p_lingo IS NOT NULL THEN -- Open the cursor source_cursor := DBMS_SQL.open_cursor; -- Create a query string to get languages based on parameters. l_select_statement := 'SELECT language_code FROM fnd_languages where nls_language = UPPER(:p_language)'; DBMS_SQL.parse (source_cursor, l_select_statement, DBMS_SQL.v7); DBMS_SQL.bind_variable (source_cursor, ':p_language', p_lingo); -- Execute the cursor DBMS_SQL.define_column (source_cursor, 1, l_lang, 30); l_dummy := DBMS_SQL.EXECUTE (source_cursor); -- If the cursor has returned more than 1 row then -- get the output of the cursor into respective variables IF DBMS_SQL.fetch_rows (source_cursor) <> 0 THEN DBMS_SQL.COLUMN_VALUE (source_cursor, 1, l_lang); l_lang_str := l_lang; ELSE -- If the cursor returned 0 rows then return the base language l_lang_str := l_base_lang; END IF; -- Close the cursor DBMS_SQL.close_cursor (source_cursor); ELSE -- If the user has not entered any value then return the base language l_lang_str := l_base_lang; END IF; fnd_file.put_line (fnd_file.LOG, 'Checking to see if the derived language has a translated layout or not' ); BEGIN -- Check if the language entered by the user is associated to a translated template or not SELECT 1 INTO l_trns_lang_check FROM xdo_lobs xl WHERE xl.lob_type = 'MLS_TEMPLATE' AND xl.trans_complete = 'Y' AND xl.LANGUAGE = l_lang_str AND xl.lob_code = ( -- Get the actual program name from the MLS request SELECT argument2 -- Prog name FROM fnd_run_req_pp_actions WHERE parent_request_id = fnd_global.conc_request_id -- Request id of the MLS function AND action_type = 6) -- Template Code ; EXCEPTION WHEN OTHERS THEN -- If the chosen language does not have an associated template the SQL will fail -- and therefore return the default language fnd_file.put_line (fnd_file.LOG, 'There is no layout for language: ' || l_lang_str ); fnd_file.put_line (fnd_file.LOG, 'Therefore we are using the default template for language: ' || l_base_lang ); l_lang_str := l_base_lang; END; RETURN (l_lang_str); EXCEPTION WHEN OTHERS THEN DBMS_SQL.close_cursor (source_cursor); RAISE; END get_lang;END xx_mls_lang;/
Step 2: Create an executable for Multi Language
When the multi language packs are installed in Oracle a new type of concurrent executable is created, Multi Language Function. We shall create a concurrent executable of this type for the database function we have created.

Step 3: Add the parameter to the concurrent program (Optional)
In this step we are going to modify the seeded program, Active Users, to provide the output in multi language. Since this program does not take any parameters we are going to add a parameter to this program to accept a language name as a user entry (as explained in Step 1).
 Step 4: Attach the multi language executable
Now we shall attach the multi language executable to the concurrent program, Active Users, so that the output language is taken from the MLS function.
Once the language packs are installed a field named, MLS function, is enabled on concurrent program form. Enter the MLS executable here.
Step 4: Attach the multi language executable
Now we shall attach the multi language executable to the concurrent program, Active Users, so that the output language is taken from the MLS function.
Once the language packs are installed a field named, MLS function, is enabled on concurrent program form. Enter the MLS executable here.
 Note: MLS function field has a LOV attached to it. The LOV has the list of executables that are of type Multi Language Function, i.e. executables defined as in Step 2.
Note: MLS function field has a LOV attached to it. The LOV has the list of executables that are of type Multi Language Function, i.e. executables defined as in Step 2.
Test the concurrent program
Now we shall execute the concurrent program to check the output. Open the SRS form
 Now select the program as Active Users.
Now select the program as Active Users.
 We get a prompt for the parameter we had created, i.e. Language. Enter a language, say Spanish.
We get a prompt for the parameter we had created, i.e. Language. Enter a language, say Spanish.
 Press OK and submit the program.
Press OK and submit the program.
 Notice that 2 concurrent programs are executed by Oracle instead of 1.
Notice that 2 concurrent programs are executed by Oracle instead of 1.
- Active Users (Multiple Languages)
- ES-ES: (Active Users)
This is because the first request is for the MLS language function and the second request is for the concurrent program.
When the concurrent programs complete check the log and output of both the requests.
- Output of request, Active Users (Multiple Languages)
 There is no output of the request that is kicked off for the MLS function.
There is no output of the request that is kicked off for the MLS function.
- Log of request, Active Users (Multiple Languages)
+---------------------------------------------------------------------------+
Application Object Library: Version : 12.0.0
Copyright (c) 1979, 1999, Oracle Corporation. All rights reserved.
FNDMLSUB module: Multiple Languages
+---------------------------------------------------------------------------+
Current system time is 15-AUG-2013 08:35:59
+---------------------------------------------------------------------------+
**Starts**15-AUG-2013 08:35:59
**Ends**15-AUG-2013 08:35:59
+---------------------------------------------------------------------------+
Start of log messages from FND_FILE
+---------------------------------------------------------------------------+
+---------------------------------------------------------------------------+
Calling language function xx_mls_lang.get_lang : 15-AUG-2013 08:35:59
Language function returned the following languages : E . : 15-AUG-2013 08:35:59
+---------------------------------------------------------------------------+
The following are the details of submitted requests:
Request ID Language
------------------------------------------
57613357 SPANISH
+---------------------------------------------------------------------------+
End of log messages from FND_FILE
+---------------------------------------------------------------------------+
Important: When a concurrent request gives output in multiple languages it is the header or the data labels that are changed into different languages. The data remains in the same language as it is stored in the database.
- Log of request, Active Users (Multiple Languages)
+---------------------------------------------------------------------------+
Application Object Library: Version : 12.0.0
Copyright (c) 1979, 1999, Oracle Corporation. All rights reserved.
FNDSCURS module: Usuarios Activos
+---------------------------------------------------------------------------+
Hora actual del sistema: 15-AGO-2013 08:35:59
+---------------------------------------------------------------------------+
+-----------------------------
| Iniciando la ejecución del programa simultáneo...
+-----------------------------
Argumentos
------------
Language='Spanish'
------------
APPLLCSP Environment Variable set to :
Current NLS_LANG and NLS_NUMERIC_CHARACTERS Environment Variables are :
SPANISH_SPAIN.UTF8
' '
Introduzca la Contraseña:
REP-0092: Advertencia: Argumento LANGUAGE versión 1.1 no soportado. Use en su lugar la variable de entorno de Idioma Nacional de ORACLE.
REP-0092: Advertencia: Argumento LANGUAGE versión 1.1 no soportado. Use en su lugar la variable de entorno de Idioma Nacional de ORACLE.
Report Builder: Release 10.1.2.3.0 - Production on Jue Ago 15 08:36:02 2013
Copyright (c) 1982, 2005, Oracle. All rights reserved.
+---------------------------------------------------------------------------+
Inicio del log de mensajes de FND_FILE
+---------------------------------------------------------------------------+
+---------------------------------------------------------------------------+
Fin del log de mensajes de FND_FILE
+---------------------------------------------------------------------------+
Note that the log file has now changed to Spanish. This means that MLS affects data labels, headers and log files but not data.
Appendix:
Now if we were to take off the MLS function from Step 4 and executed Active Users concurrent program then Oracle would have executed only 1 request.

-
FND_LANGUAGES table shows which languages are installed, and which is the base language and which are non-base languages (Installed Languages)Query to identify which language(s) have been installed

- The Translated tables (*_TL) contain one record for each language i.e the translated string for each language.
- Translated views (*_VL) have been introduced for the “_TL” tables, which allow concurrent programs to select data based on the session language without running the risk of returning more rows than expected using a condition within the view query like,t.LANGUAGE= USERENV(‘LANG’)
If queries are executed from SQL*Plus on the _VL views without setting the session language then no rows will be returned. This is explained in this article.


MLS development guidelines
User messages
- All user message (labels/pop ups) are to be derived from translation tables or from fnd message.
- Form item labels
- Report item labels
- Pop up messages
- Concurrent program output
- Workflow notifications
- Form personalizations


SQL Queries
-
SQL queries should access data from _TL tables or _VL tables and have the following WHERE clauset.LANGUAGE= USERENV(‘LANG’)
XML Publisher reports
- There are 2 ways to develop XML Publisher report templates
- Each report will have as many templates as the number of languages it is expected to run on.
- Single template across all languages where the labels will also be derived from fnd messages or translation tables
Single template Multiple template Advantage - 1 single file to be maintained
- Modification/Addition of business logic or layout is simple
- No business logic required to display template associate with language. It is configured in Oracle.
Disadvantage - Modification/Addition of business logic or layout in the template is difficult
- Business logic required to display the template associated with the language
- Multiple files to be maintained


SQL Loader
-
To include different character sets into an Oracle table we have to specify the character set in the control file.ExampleLOAD DATACHARACTERSET UTF8INFILE *REPLACE INTO TABLE LOADER_TESTFIELDS TERMINATED BY ‘;’TRAILING NULLCOLS (USR_ID INTEGER EXTERNAL,USR_NAME CHAR(50),USR_LNK_NAME CHAR(50),USR_LNK_ORDER INTEGER EXTERNAL)BEGINDATA1;Santé bien;http://www.vaud-sante.ch;32;Santé;http://www.vaud-sante.ch;43;Alle à gessa;http://www.gessa.com/now;24;Alle à;http://www.gessa.com/now;15;Gägs;http://www.gaegs.ch;56;Gägs ä;http://www.gaegs.ch;6
Application File System
-
Once the MLS patches have been applied to Oracle a set of directories are created in Unix under reports, forms, etc directories with the 2 character language code.
- For instance, if patch for Spanish has been applied in Oracle a new set of folders will be created, like $GL_TOP/reports/ES, $AP_TOP/forms/ES
- The point to keep in mind here is that any custom component created with specific changes for a language must be dropped to the language specific directory.
- All translatable files reside in a subdirectory which has the language code incorporated in the name (e.g. $AP_TOP/reports/EL, $GL_TOP/forms/F etc.) .
– Forms, Reports, Messages & Seeded data are translated

NLS parameters in functions
-
TO_DATE
- NLS_DATE_LANGUAGE
- NLS_CALENDAR
-
TO_NUMBER
- NLS_NUMERIC_CHARACTERS
- NLS_CURRENCY
- NLS_DUAL_CURRENCY
- NLS_ISO_CURRENCY
-
TO_CHAR
- NLS_DATE_LANGUAGE
- NLS_NUMERIC_CHARACTERS
- NLS_CURRENCY
- NLS_ISO_CURRENCY
- NLS_DUAL_CURRENCY
- NLS_CALENDAR
-
TO_NCHAR
- NLS_DATE_LANGUAGE
- NLS_NUMERIC_CHARACTERS
- NLS_CURRENCY
- NLS_ISO_CURRENCY
- NLS_DUAL_CURRENCY
- NLS_CALENDAR
-
NLS_UPPER
- NLS_SORT
-
NLS_LOWER
- NLS_SORT
-
NLS_INITCAP
- NLS_SORT
-
NLSSORT
- NLS_SORT
Example of usage

Example of error message after applying MLS patches

- The LOV associated with the DFF segment has not been correctly coded with regards to translations.
- We can add LANGUAGE= USERENV(‘LANG’) in the Where/Order By region to pick up the value based on the user’s language
- We can change the table name to FND_LOOKUP_VALUES_VL instead of FND_LOOKUP_VALUES
- Site
- Application
- Responsibility
- Server
- Server with Responsibility
- Organization
- User
When needed one and the same profile option can be assigned to different levels. For example, when you implement Global Security Profiles to create access control on Operation Units – every responsibility for an Operating Unit may need a setting for profile options MO: Security Profile and HR: Security Profile. In the form which is used to set profile options all those different responsibilities can’t be seen at once.
In that case I use the SQL statement below to quickly provide me a list of the values of a profile option for all levels.
The profile option name (column profile_option_name from table applsys.fnd_profile_options) can be found within the definition of the profile itself through responsibility Application Developer – menu Profile.
Here’s the SQL to provide you the values on all levels of a specific profile.
SELECT
SUBSTR(e.profile_option_name,1,25) INTERNAL_NAME,
SUBSTR(pot.user_profile_option_name,1,60) NAME_IN_FORMS,
DECODE(a.level_id,10001,’Site’,10002,’Application’,10003,’Resp’,
10004,’User’,10005,’Server’,10007,’Server+Resp’,a.level_id) LEVELl,
DECODE(a.level_id,10001,’Site’,10002,c.application_short_name,
10003,b.responsibility_name,10004,d.user_name,10005,n.node_name,
10007,m.node_name||’ + ‘||b.responsibility_name,a.level_id) LEVEL_VALUE,
NVL(a.profile_option_value,’Is Null’) VALUE,
to_char(a.last_update_date, ‘DD-MON-YYYY HH24:MI’) LAST_UPDATE_DATE,
dd.USER_NAME LAST_UPDATE_USER
FROM
applsys.fnd_profile_option_values a,
applsys.fnd_responsibility_tl b,
applsys.fnd_application c,
applsys.fnd_user d,
applsys.fnd_profile_options e,
applsys.fnd_nodes n,
applsys.fnd_nodes m,
applsys.fnd_responsibility_tl x,
applsys.fnd_user dd,
applsys.fnd_profile_options_tl pot
WHERE
e.profile_option_name = ‘XLA_MO_SECURITY_PROFILE_LEVEL’ AND e.PROFILE_OPTION_NAME = pot.profile_option_name (+)
AND e.profile_option_id = a.profile_option_id (+)
AND a.level_value = b.responsibility_id (+)
AND a.level_value = c.application_id (+)
AND a.level_value = d.user_id (+)
AND a.level_value = n.node_id (+)
AND a.LEVEL_VALUE_APPLICATION_ID = x.responsibility_id (+)
AND a.level_value2 = m.node_id (+)
AND a.LAST_UPDATED_BY = dd.USER_ID (+)
AND pot.LANGUAGE = ‘US’
ORDER BY
e.profile_option_name
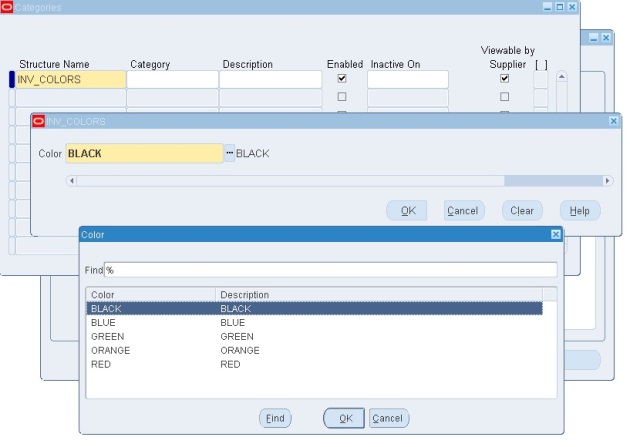
- Item1 —- Black
- Item2 —- Red
- Item3 —- Green
- Item4 —- Orange
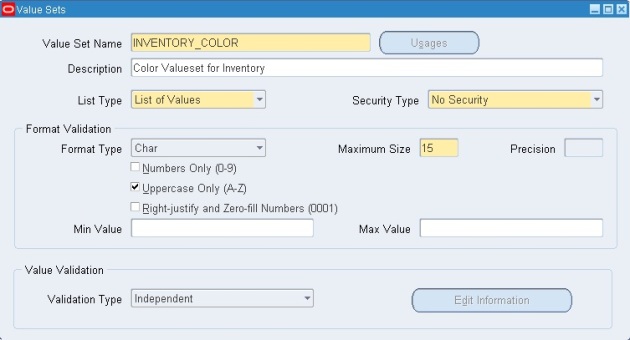
- Enter the “Number” field: 10
- Enter the Name field: Color
- Enter the “Window Prompt”: Color (This value will appear on the screen)
- Enter the “Column” field: Segment1 (you can choose any column)
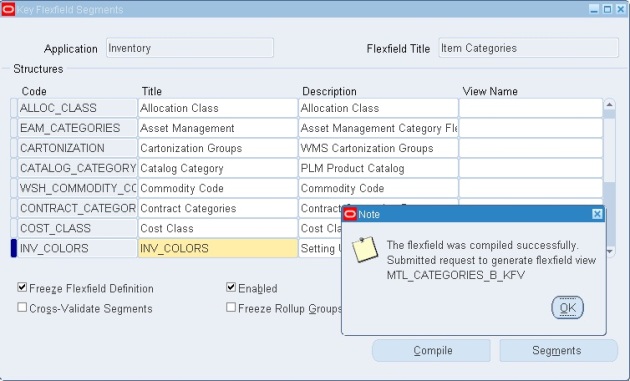
- Enter the structure name: INV_COLORES
- Enter the category: BLACK
- (Note the form does not provide an LOV for the categories. You will need to use edit symbol at the top of the page or “ e “ to bring up the lov)
- Enter the description.
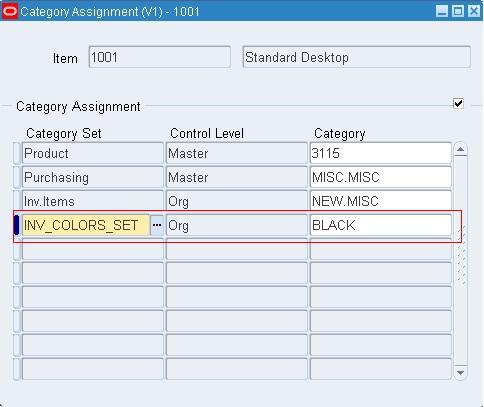
- Fill in the category set Name: INV_COLORS_SET
- The description: Inventory color set
- The Flex Structure: INV_COLORS
- The Controlled: Org Level
- Default Category: BLACK
Latest Posts
- R12 – How to Handle NULL for :$FLEX$.VALUE_SET_NAME In Oracle ERPAugust 25, 2023 - 1:20 pm
- R12 – How to Delete Oracle AR TransactionsMarch 22, 2019 - 8:37 pm
- How to Define Custom Key Flexfield (KFF) in R12January 19, 2018 - 5:43 pm
- AutoLock Box Concepts In R12November 10, 2017 - 8:30 am
- R12 – java.sql.SQLException: Invalid column type in OAFSeptember 15, 2017 - 9:39 am








Recent Comments