The focus of the document is for consultants who are new to Oracle Forms and needs a kick-start on the concepts for better understanding of the subject.
Let’s start understanding the basic but important concepts in Forms.
What is Form :It is a developmental tool that is used for designing data entry and query screens. It is a front-end tool that runs in a Graphical User Interface (GUI).
GUI Concepts:
These concepts holds good for any user-interface.
To develop an effective GUI there are 4 basic stages:
- Define User Requirements
- Plan the User Interface
- Build the User Interface Elements (Create/Modify elements/functionality)
- User Feedback (Holds Key on the functionality and basis of the requirement)
Let’s move on to Forms Developer
How many components in Forms?
There are 3 components involved in the application development
- Form Builder
- Form Compiler
- Form Runtime
Form builder consists of following tools to perform a specific task
- Object Navigator
- Layout Editor
- Property Palette
- PL/SQL Editor
- Menu Editor
- Object Library
Object Navigator: It’s a hierarchal representation of all objects.
Layout Editor: It provides a virtual representation of the application user interface.
Property Palette: Each object in the form module has a property associated to it. Developer can view/set properties for one/multiple object.
PL/SQL Editor: Programmatically to enhance the functionality and appearance of an application.
Menu Editor: Create menu as per applications requirement and can add various functionality to various menu options.
Object Library: Creation of objects on some default specification. Storing some standard objects that can be re-used in other forms/menu.
Blocks: Logically related interface items are grouped into functional units called Blocks.
Types of Block:
Data Block: It is associated with or bound, to a database table or view or a set of stored procedures.
Control Block: It is not associated with any database table but items that will control the behavior of the application.
Let’s move on to the next scheme of things…
Canvas: It is a surface inside a window on which we place the interface that end user interacts.
Types of Canvas:
- Stacked Canvas
- Content Canvas
- Horizontal Toolbar
- Vertical Toolbar
- Tab Canvas
Let’s discuss briefly about the triggers in this section, for more information you can look through the Forms Builder Help Topics.
Note: The hierarchy of Objects in a form is
Form
Block
Record
Item
What is Triggers: These are program units which enhance the functionality of a form/application.
The following triggers can be used to enhance the functionality of the form:
What are Types of triggers in Oracle Form?
Block Processing Triggers: It fires in response to events related to record management in block.
e.g., When_Create_Record,When_Clear_Block,…
Interface Event Triggers: It fires in response to events that occur in form interface.
e.g., When_Button_Pressed,When_Checkbox_Changed,…
Master-Detail Triggers: It fires automatically when defined master-detail relationship between blocks. (Master-Detail relationship discussed further in the document)
e.g.,On_Checkdelete_Master,On_Clear_Details,…
Message Handling Triggers: It fires to issue appropriate error and information messages in response to runtime events.
e.g.,On_Error,On_Message,..
Navigational Triggers: It fires in response to Navigational Items.
e.g., Pre_Form, Post_Form, When_New_Form_Instance, When_New_Block_Instance,..
Query Time Triggers: It fires before/after the operator/application executes a query.
e.g.,Pre_Query,Post_Query,…
Transactional Triggers: It fires in response to wide variety of events that occur as a form interacts with data source.
e.g.,On_Delete,On_Update,..
Validation Triggers: It fires when it validates data in an item/record.
e.g.,When_Validate_Item,When_Validate_Record,..
Mouse Event Triggers: It fires for a mouse event.
e.g.,When_Mouse_Enter,When_Mouse_Click,..
Key Triggers: It has one to one relationship with specific Keys.
e.g.,Key F1,Key Enter,..
There are lot number triggers that can be used, please use as per the requirement with reference to Form Builder Help Topics.
What is Master- Detail Relationship? or What is Parent -Child Relationship?
Master- Detail Relationship : It is an association between two datablocks.One block is called Master Block and other Detail block. The relationship signifies that there is a primary key to foreign key relationship between the tables on the blocks associated.
What are Properties associated with blocks in a master-detail relationship?
Isolated : If you delete master records, associated detail records are not deleted from the database.
Non-Isolated: You cannot delete master records if the associated detail records exist in database.
Cascading: If you delete master records then automatically detail records will be automatically deleted from the database.
Windows : It is a container for all visual objects that make up a form, including canvases.
There are 2 types of Windows:
Document Window : It typically display the main canvases and work areas of the application where most data entry, and data retrieval is performed. It always remains within the application window frame.
Dialog Window: are free-floating, windows typically used for modal dialogs that require immediate user interaction.
Modality of the window depends on the functionality required i.e., Modal or Modeless.
Alert : It is a modal window that displays message to inform user about some application condition. E.g., STOP,CAUTION,NOTE,…
Invoking an alert : show_alert(alert_name)
Return number;
What is Record Group: It is an internal form builder structure that has column/row structure similar to database table. Static and Query based record groups can be used on the functionality of the form.
What is List of Values (LOV) : It is a pop-up window that provides end user selection list. LOV’s can be invoked programmatically or statically based on the record group. It can be positional based or automatic display.
The most important features of LOV are it provides auto-reduction and search features due to which user can locate specific values easily.
Let’s get to items on canvas which holds the key points.
Boilerplate Text Tool is used to create or edit a graphics text in the form. Graphics text is a static text in the form. E.g. Labels for items
Text Item Tool is used to create text item. It is an interface control that displays and allows editing of a text. It can be single or multi-line format.
Display Item tool are similar to text items but display items only store and displayed fetched or assigned values.
Buttons is a tool to execute commands or initiate buttons. E.g., OK ,CANCEL,..
Types : Text and Iconic Buttons
List Item is a list of text elements. A list item displays a fixed number of elements.
Types: Tlist,Pop List, Combo Box
Checkbox: It is a control that has 2 states i.e., checked or unchecked. It is used to indicate whether a certain condition is true or false.
Radio Button/Box : It is a logical set of options.
Editors: are used to edit item values in form. There are three editors that can be used at run time: Default editor, System Editor, User Named Editor
Property Class: Form builder provides a facility to create a named list of common properties and their values. This object is known as property class. Once you create a property class, you can base other objects on it. It is similar to the OOPS concept in programming languages.
Visual attribute : is a list of font, color and pattern properties and their values. This visual attribute can be attached to various objects to define object’s visual attributes.



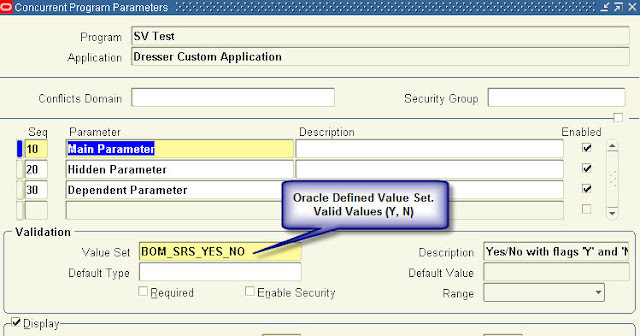
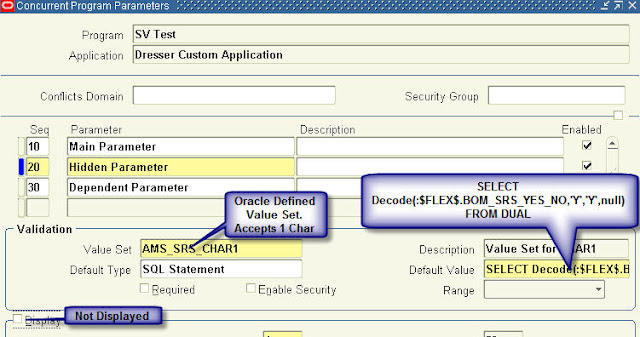
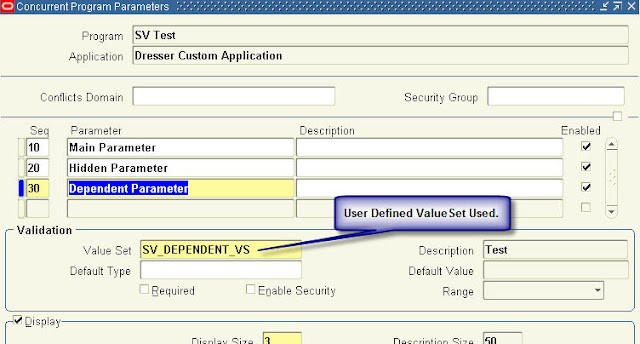
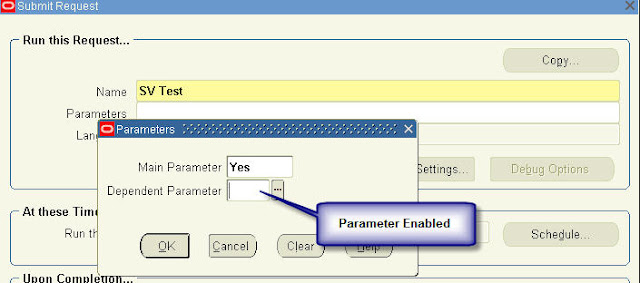
Recent Comments