Now, legal Entities can be mapped to entire Ledgers or if you account for more than one legal entity within a ledger, you can map a legal entity to balancing segments within a ledger.
While a set of books is defined by 3Cs
- chart of accounts
- functional currency
- accounting calendar,
The addition in this list the ledger is defined by a 4th C: the accounting method.
This 4th C allows you to assign and manage a specific accounting method for each ledger. Therefore, when a legal entity is subject to multiple reporting requirements, separate ledgers can be used to record the accounting information.
Accounting Setup Manager is a new feature that allows you to set up your common financial setup components from a central location.
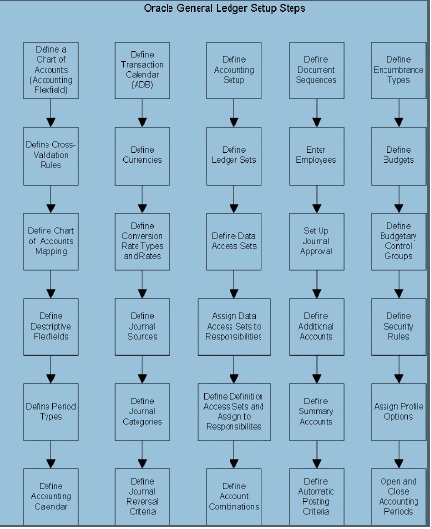
General Ledger Setup Flowchart
While you can set up your Oracle General Ledger application in many different ways, and defer optional set up steps until you are ready to use the corresponding functionality, we recommend you use the order suggested in the following flowchart: Some of the steps outlined in this flowchart and setup checklist are Required and some are Optional. You need to perform Optional steps only if you plan to use the related feature or complete certain business functions.
The following setup steps are a high level overview of the setup steps related to Oracle
General Ledger and Accounting Setup Manager.
5. Assign Balancing Segment Values to respective Legal entities.
- Create legal entity
- Define Leger
Click on Next and then Finish.
- Define Accounting Options
Click on Define Accounting Options and click on update.
Click on Next, and assign Retained earnings Account.
Click on Next, Next, and Finsh.
Assign Legal entities to your Ledger.
Click on Add Legal entity.
Add your Legal entity and click on Apply.
- Assign Balancing segment values to legal entities
Click on the update Balancing Segment Values
Click on Add Balancing Segment Value.
Assign Balancing segment values to these legal entities.
Click on Apply and then click onComplete.
Once you complete ledger we are getting the following Warning.
Click on Yes.
Ofter click on the yes we are getting the following confirmation.
Click on Return to Accounting Setups.














 Options in 11i To Options in 12
Options in 11i To Options in 12 Out of the box, Oracle seeds accounting rules for all applications. If you are satisfied with the Oracle’s seeded rules, there is no need to change any setup and you can use those existing rules (Accounting Method for Accrual is Standard Accrual and for Cash is Standard Cash). This screenshot here shows you the difference between the Accrual Basis of accounting and Cash Basis of Accounting. As you can see here, per rules, there is no accounting created when invoice is created under cash basis (no revenue is recognized until cash is received) but accounting is created when cash is realized. Invoice is accounted as soon it is completed under Accrual Method. This is configurable here where as in 11i we did not have a choice!.
Out of the box, Oracle seeds accounting rules for all applications. If you are satisfied with the Oracle’s seeded rules, there is no need to change any setup and you can use those existing rules (Accounting Method for Accrual is Standard Accrual and for Cash is Standard Cash). This screenshot here shows you the difference between the Accrual Basis of accounting and Cash Basis of Accounting. As you can see here, per rules, there is no accounting created when invoice is created under cash basis (no revenue is recognized until cash is received) but accounting is created when cash is realized. Invoice is accounted as soon it is completed under Accrual Method. This is configurable here where as in 11i we did not have a choice!.
 Starting R12 all accounting entries are generated and passed through subledger accounting application instead of directly going to GL. Hence reconciliation is already done between source to Subledger Accounting and Subledger Accounting to GL, reducing huge amount of time spent on reconciliation. Since these entries have to flow through the subledger accounting application, there is a need to map the source application accounting entries to subledger accounting. That is key for the setups.
Starting R12 all accounting entries are generated and passed through subledger accounting application instead of directly going to GL. Hence reconciliation is already done between source to Subledger Accounting and Subledger Accounting to GL, reducing huge amount of time spent on reconciliation. Since these entries have to flow through the subledger accounting application, there is a need to map the source application accounting entries to subledger accounting. That is key for the setups. AR Invoice Accounting
AR Invoice Accounting Taking a step back and thinking through, this transaction is happening in AR for the Invoice Creation event….
Taking a step back and thinking through, this transaction is happening in AR for the Invoice Creation event….  Now we map the source (AR Invoices) to Subledger Accounting as shown here. So to conclude
Now we map the source (AR Invoices) to Subledger Accounting as shown here. So to conclude
Recent Comments